Imagine planting a single lily pad in a pond. It doubles every day. By day 30, the pond is completely covered. Here’s the mind-bending part: on which day was the pond half covered? Day 29. That’s the power of exponential growth; it sneaks up on you, then explodes.
In simple terms, exponential growth means something increases by a fixed percentage over equal time periods, creating a snowball effect where the growth accelerates over time. Unlike linear growth (where you add the same amount each period), exponential growth multiplies, leading to dramatic results that can transform your wealth, or catch you off guard if you’re on the wrong side of it. The Motley Fool
For investors, understanding exponential growth isn’t just academic; it’s the secret sauce behind compound interest, stock market returns, and building generational wealth. It’s why starting early matters so much, and why small differences in return rates create massive gaps in outcomes over decades.
Whether you’re trying to grow your wealth through dividend investing or understand why the stock market tends to go up over time, grasping exponential growth will fundamentally change how you think about money and investing.
TL;DR Summary
- Exponential growth occurs when something increases by a fixed percentage over time, causing accelerating growth that compounds on itself
- Consistency beats timing—regular contributions combined with compound growth outperform trying to time the market
- Starting early is crucial because exponential growth needs time to work its magic—waiting even 5-10 years can cost you hundreds of thousands of dollars
- The Rule of 72 helps estimate doubling time: divide 72 by your annual return rate to see how long it takes to double your money
- Compound interest is exponential growth in action—earning returns on your returns creates wealth acceleration
- Time is the most powerful variable in exponential growth—the longer your money compounds, the more dramatic your results become
What Is Exponential Growth? The Definition That Matters
Exponential growth is a pattern where a quantity increases by a constant percentage during equal time intervals, causing the rate of growth to accelerate over time.
Here’s what makes it different from linear growth:
| Growth Type | How It Works | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Growth | Add the same amount each period | Save $1,000 per year: Year 1 = $1,000, Year 2 = $2,000, Year 3 = $3,000 |
| Exponential Growth | Multiply by the same percentage each period | Invest $1,000 at 10% annual return: Year 1 = $1,100, Year 2 = $1,210, Year 3 = $1,331 |
The mathematical formula for exponential growth is:
Final Value = Initial Value × (1 + Growth Rate)^Time
Where:
- Initial Value = your starting amount
- Growth Rate = the percentage increase per period (expressed as a decimal)
- Time = number of periods
- ^ = “raised to the power of”
For example, if you invest $10,000 at a 7% annual return for 30 years:
$10,000 × (1.07)^30 = $76,123
That’s more than 7.6 times your initial investment!
The Power of Compound Interest: Exponential Growth in Action
Compound interest is exponential growth applied to your money. In simple terms, compound interest means earning returns on your returns, creating a snowball effect that accelerates your wealth over time.
Here’s a real-world story that illustrates the power: Meet Sarah and Tom, both 25 years old.
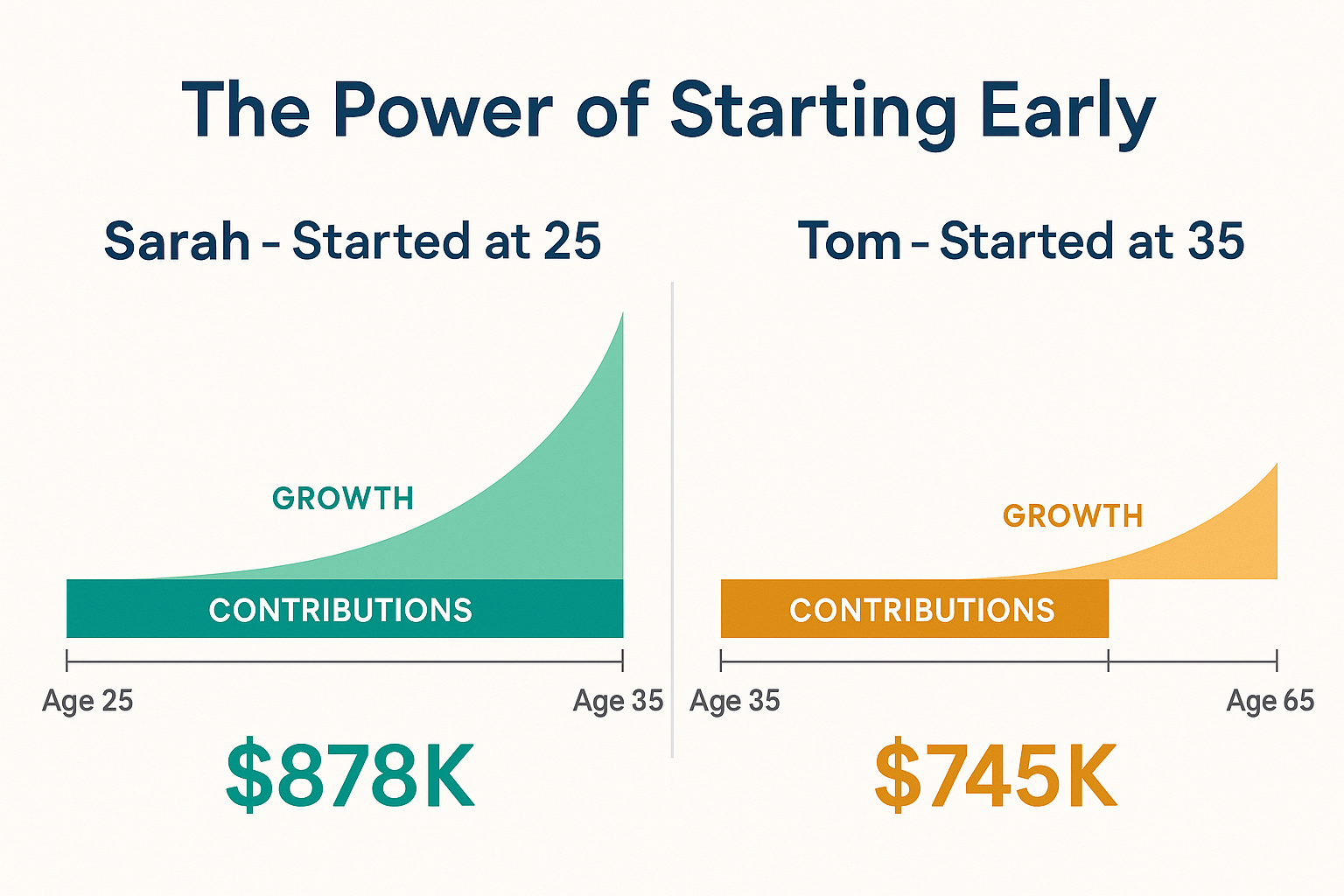
Sarah’s approach:
- Invests $500/month starting at age 25
- Stops contributing at age 35 (invested for 10 years)
- Total contributed: $60,000
- Let it grow until age 65 (30 more years of growth)
- Average annual return: 8%
Tom’s approach:
- Waits until age 35 to start investing
- Invests $500/month from age 35 to 65 (30 years)
- Total contributed: $180,000
- Average annual return: 8%
The shocking result?
Sarah ends up with approximately $878,000, while Tom has about $745,000—despite contributing only one-third as much money!
This demonstrates why making your kid a millionaire through early investing is so powerful.
The Three Components of Compound Growth
- Principal (your initial investment)
- Time (how long it compounds)
- Rate of return (your growth percentage)
The magic happens when these three factors work together. Change any one of them, and you dramatically alter the outcome.
The Rule of 72: Your Quick Exponential Growth Calculator
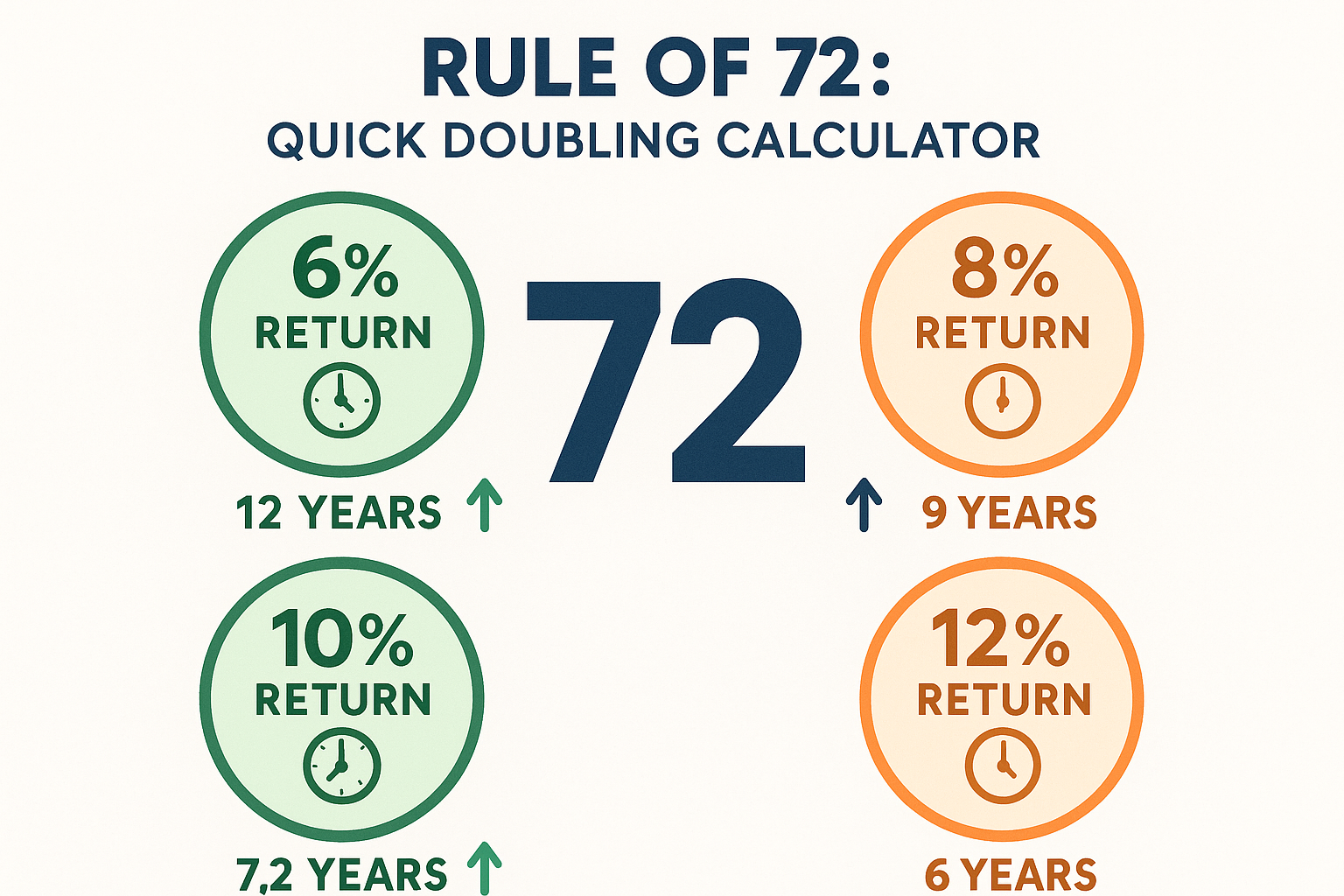
The Rule of 72 is a mental shortcut that helps investors estimate how long it takes to double their money.
The formula: 72 ÷ Annual Return Rate = Years to Double
Examples:
- 6% annual return: 72 ÷ 6 = 12 years to double
- 8% annual return: 72 ÷ 8 = 9 years to double
- 10% annual return: 72 ÷ 10 = 7.2 years to double
- 12% annual return: 72 ÷ 12 = 6 years to double
This simple rule helps you quickly understand the power of different return rates. A seemingly small difference between 6% and 10% means your money doubles in half the time, and over multiple doubling periods, this creates enormous wealth gaps.
Real-World Application
Let’s say you’re comparing two investment options:
- Option A: 7% annual return
- Option B: 9% annual return
Using the Rule of 72:
- Option A doubles in 10.3 years
- Option B doubles in 8 years
Over 40 years:
- Option A doubles approximately 3.9 times (turning $10,000 into about $150,000)
- Option B doubles approximately 5 times (turning $10,000 into about $314,000)
That 2% difference created an extra $164,000!
How Investors Can Harness Exponential Growth
Understanding exponential growth is one thing—using it to build wealth is another. Here’s how smart investors put this knowledge to work:
1. Start Early and Stay Consistent
Time is your most valuable asset when it comes to exponential growth. The earlier you start, the more doubling periods you capture.
Consider this powerful example:
- Investor A starts at age 25, contributes $6,000/year until age 35 (10 years), then stops
- Investor B starts at age 35, contributes $6,000/year until age 65 (30 years)
- Both earn 8% annually
Results at age 65:
- Investor A: ~$590,000 (contributed $60,000)
- Investor B: ~$680,000 (contributed $180,000)
Investor A contributed one-third of the amount but ended up with 87% of what Investor B accumulated. The 10-year head start made that much difference.
2. Reinvest Your Dividends
When you receive dividends from stocks, you face a choice: take the cash or reinvest it. Reinvesting creates exponential growth because those dividends buy more shares, which generate more dividends, which buy even more shares.
According to Hartford Funds research, reinvested dividends have accounted for approximately 40% of the total return of the S&P 500 since 1960.
If you’re interested in maximizing this strategy, check out these resources on high dividend stocks and passive income through dividend investing.
3. Maximize Your Return Rate (Within Your Risk Tolerance)
Small differences in return rates create massive differences over time due to exponential growth. However, chasing higher returns often means taking on more risk.
Historical average annual returns (1926-2023):
- Large-cap stocks: ~10%
- Small-cap stocks: ~12%
- Corporate bonds: ~6%
- Treasury bonds: ~5%
- Cash/savings: ~3%
A balanced portfolio appropriate for your age and risk tolerance is crucial. The stock market’s long-term upward trend has historically rewarded patient investors who stayed invested through volatility.
4. Avoid Withdrawals and Interruptions
Every time you withdraw money, you interrupt the exponential growth process. You’re not just losing the amount you withdraw—you’re losing all the future growth that money would have generated.
Example: Withdrawing $10,000 from a retirement account at age 35 doesn’t just cost you $10,000. At 8% annual growth, that $10,000 would have become $68,485 by age 60. The true cost is nearly 7 times what you withdrew!
5. Increase Contributions Over Time
As your income grows, increasing your investment contributions accelerates exponential growth. Even small increases make a significant difference.
Scenario: Start with $500/month at age 30, increase by just $50/month each year
- By age 65 at 8% return: ~$2.1 million
- Same starting amount but no increases: ~$1.1 million
That’s an extra million dollars from gradually increasing contributions!
Real Data Example: The S&P 500 and Exponential Growth
Let’s look at real historical data to see exponential growth in action. The S&P 500 provides an excellent case study.
If you invested $10,000 in the S&P 500 on January 1, 1980:
| Year | Approximate Value |
|---|---|
| 1980 | $10,000 |
| 1990 | $45,000 |
| 2000 | $145,000 |
| 2010 | $163,000* |
| 2020 | $430,000 |
| 2025 | $750,000+ |
*The 2000-2010 period included two major crashes (the dot-com bubble and 2008 financial crisis), demonstrating that exponential growth isn’t smooth, but it persists over long periods.
This represents an average annual return of approximately 10%, turning $10,000 into over $750,000 in 45 years through the power of exponential growth and compound returns.
Understanding why people lose money in the stock market often comes down to not respecting this long-term exponential pattern and instead reacting to short-term volatility.
Exponential Growth vs Linear Growth: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Understanding the difference between these two growth patterns is fundamental to investment success.
Linear Growth Example: Saving Cash
You save $5,000 per year in a safe at home (0% return):
- Year 10: $50,000
- Year 20: $100,000
- Year 30: $150,000
- Year 40: $200,000
Growth pattern: Straight line, predictable, consistent additions
Exponential Growth Example: Investing with Returns
You invest $5,000 per year at 8% annual return:
- Year 10: $78,227
- Year 20: $247,115
- Year 30: $611,729
- Year 40: $1,398,905
Growth pattern: Slow at first, then curves upward dramatically
The difference by year 40? Nearly $1.2 million more with exponential growth!
The J-Curve Effect
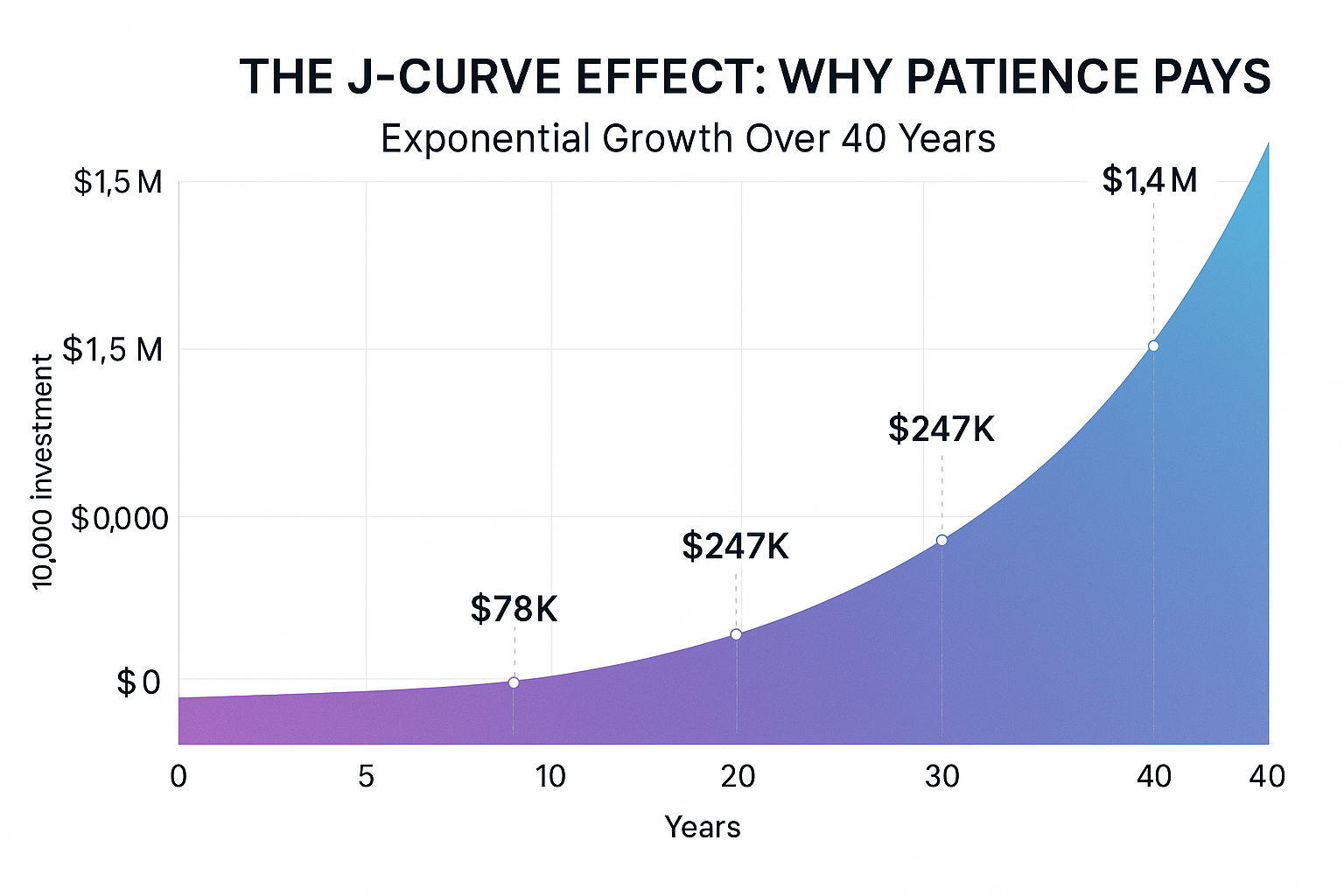
Exponential growth creates what’s called a J-curve; it looks flat for a long time, then suddenly shoots upward. This is why:
- Early years feel slow: Your account balance doesn’t seem to grow much
- Middle years build momentum: Growth becomes more noticeable
- Later years are explosive: Most of your wealth accumulates in the final decade or two
This pattern frustrates many new investors who expect immediate, dramatic results. Understanding the J-curve helps you stay patient during the crucial early accumulation phase. Corporate Finance Institute
Advantages and Limitations of Exponential Growth in Investing
Advantages
1. Wealth Multiplication
Exponential growth transforms modest contributions into substantial wealth over time, making millionaire status achievable for average earners who start early.
2. Passive Acceleration
Once set in motion, exponential growth works automatically—your money works for you 24/7 without additional effort.
3. Inflation Protection
Investments that grow exponentially typically outpace inflation, preserving and increasing your purchasing power over time.
4. Democratizes Wealth Building
You don’t need to be rich to benefit—even small amounts grow substantially when given enough time and consistent contributions.
5. Rewards Patience
The longer you stay invested, the more dramatic your results become, creating an incentive for long-term thinking.
Limitations and Risks
1. Requires Time
Exponential growth needs years or decades to produce dramatic results; it’s not a get-rich-quick strategy.
2. Not Guaranteed
Historical averages don’t guarantee future returns. Markets fluctuate, and actual returns vary significantly from year to year.
3. Vulnerable to Interruptions
Withdrawals, stopping contributions, or panic-selling during downturns can severely damage exponential growth.
4. Inflation Impact
While growth may be exponential in nominal terms, inflation reduces real purchasing power; a 7% return with 3% inflation equals 4% real growth.
5. Sequence of Returns Risk
The order in which you experience returns matters, especially near retirement. Poor returns early can significantly impact outcomes.
6. Behavioral Challenges
The slow start of exponential growth tests investor patience. Understanding the cycle of market emotions helps navigate psychological challenges.
Common Mistakes That Sabotage Exponential Growth
Even investors who understand exponential growth often make critical mistakes that undermine their results:
1: Starting Too Late
The cost of delay: Waiting just 10 years to start investing can reduce your final wealth by 50% or more, even if you contribute more total dollars later.
Solution: Start immediately, even with small amounts. $100/month starting today beats $500/month starting in five years.
2: Withdrawing Early
Taking money out before retirement interrupts the compounding process and costs you all future growth on that amount.
Solution: Treat retirement accounts as untouchable except in genuine emergencies. Build a separate emergency fund for unexpected expenses.
3: Stopping Contributions During Market Downturns
When markets drop, many investors stop contributing or even sell, exactly when they should be buying at lower prices.
Solution: Maintain consistent contributions regardless of market conditions. Dollar-cost averaging means you buy more shares when prices are low.
4: Chasing Higher Returns Without Understanding Risk
Pursuing maximum returns often leads to taking excessive risk, which can result in devastating losses that set back exponential growth by years.
Solution: Choose an appropriate asset allocation for your age and risk tolerance. Consistent 8% returns beat volatile swings between +20% and -15%.
5: Ignoring Fees and Expenses
High management fees compound negatively, eating away at your exponential growth. A 2% annual fee might not sound like much, but over 40 years, it can reduce your final balance by 40% or more.
Solution: Choose low-cost index funds and ETFs. Every 0.5% you save in fees adds thousands or tens of thousands to your final balance.
6: Not Reinvesting Dividends
Taking dividends as cash instead of reinvesting them eliminates a significant source of exponential growth.
Solution: Set dividends to automatically reinvest. This ensures you capture the full power of compounding without having to think about it.
How to Interpret Exponential Growth in Your Investment Decisions
Understanding exponential growth should influence several key investment decisions:
1. Retirement Planning
When planning for retirement, exponential growth means:
- Front-loading contributions in your 20s and 30s is dramatically more effective than playing catch-up in your 50s
- The final 10 years before retirement will likely see more absolute dollar growth than all previous years combined
- Small increases in contribution rates early on create massive differences in outcomes
2. Asset Allocation
Exponential growth considerations affect how you allocate investments:
- Younger investors should favor higher-growth assets (stocks) because they have more doubling periods ahead
- Older investors need to protect accumulated gains, shifting toward more stable investments
- The 110-minus-age rule (110 minus your age = percentage in stocks) accounts for exponential growth timelines
3. Contribution Strategies
Maximize exponential growth through smart contribution tactics:
- Automate contributions to ensure consistency
- Increase contributions annually to accelerate growth
- Max out tax-advantaged accounts first (401k, IRA) to keep more money compounding
- Consider mega backdoor Roth strategies for high earners to maximize tax-free exponential growth
4. Evaluating Investment Opportunities
When comparing investments, exponential growth helps you understand:
- Why fees matter so much (they compound negatively)
- How small return differences create huge outcome gaps
- The value of tax efficiency (keeping more returns compounding)
- Why market timing usually fails (missing the best days interrupts exponential growth)
Exponential Growth and Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Tax-advantaged retirement accounts supercharge exponential growth by eliminating or deferring taxes that would otherwise slow compounding.
Traditional 401(k) and IRA Benefits
Tax-deferred growth means:
- No taxes on dividends, interest, or capital gains while invested
- More money stays invested and compounds
- You only pay taxes upon withdrawal in retirement
Example comparison (assuming 24% tax bracket):
Taxable account: $10,000 invested, 8% return, 30 years
- Taxes paid annually on gains
- Final value: ~$63,000
Tax-deferred account: Same parameters
- No taxes until withdrawal
- Final value: ~$100,000 (then taxed)
- After 24% tax: ~$76,000
That’s $13,000 more from tax-deferred exponential growth!
Roth IRA: Tax-Free Exponential Growth
Roth accounts offer something even more powerful: tax-free exponential growth forever.
You contribute after-tax dollars, but all future growth and withdrawals are completely tax-free. For young investors, this is incredibly valuable because:
- Your money has decades to compound
- You’ll likely be in a higher tax bracket in retirement
- All that exponential growth escapes taxation entirely
Example: $6,000/year contribution from age 25 to 65 at 8% return
- Total contributed: $240,000
- Final value: ~$1.86 million
- Taxes owed on growth: $0
That’s $1.62 million in tax-free gains thanks to exponential growth in a Roth account!
For more strategies on building wealth effectively, explore these smart moves and smart ways to make passive income.
Exponential Growth Beyond Investments
While we’ve focused on financial investments, exponential growth appears in many areas relevant to wealth building:
Business Growth and Revenue
Successful businesses often experience exponential revenue growth, especially in their early years. A company that grows revenue by 30% annually will double every 2.4 years using the Rule of 72.
This is why investing in growth companies early can be so lucrative—you’re capturing exponential business growth that translates to exponential stock price appreciation.
Skill Development and Career Earnings
Your earning power can grow exponentially through:
- Compound learning: Each skill you master makes learning the next skill easier
- Network effects: Your professional network grows exponentially as contacts introduce you to their contacts
- Career advancement: Each promotion increases your salary base, and percentage raises compound on higher amounts
Someone who increases their income by 5% annually through raises and career advancement will see their earnings double every 14.4 years—turning a $50,000 starting salary into $100,000 by mid-career.
Debt and Negative Exponential Growth
Unfortunately, exponential growth works against you with debt, especially high-interest credit card debt.
Credit card debt example:
- $10,000 balance at 18% APR
- Making minimum payments only
- Time to pay off: 30+ years
- Total interest paid: $18,000+
This is negative exponential growth—the debt compounds against you. Eliminating high-interest debt should be a priority before focusing on investment returns.
Real-World Case Study: Warren Buffett and Exponential Wealth
Warren Buffett’s wealth trajectory perfectly illustrates exponential growth in action.
Warren Buffett’s net worth by age:
- Age 25: ~$100,000
- Age 35: ~$1 million
- Age 45: ~$25 million
- Age 55: ~$376 million
- Age 65: ~$3.6 billion
- Age 85: ~$73 billion
- Age 94 (2025): ~$130+ billion
Key insight: Buffett made approximately 95% of his wealth after age 65. This isn’t because he suddenly became a better investor—it’s because exponential growth becomes most dramatic in the later years.
His average annual return of roughly 20% over six decades created this extraordinary wealth through pure exponential compounding. The lesson? Consistency plus time equals extraordinary results.
Buffett himself famously said: “My wealth has come from a combination of living in America, some lucky genes, and compound interest.”
The Mathematics Behind Exponential Growth (Simplified)
For those interested in the underlying math (don’t worry, we’ll keep it simple):
The Basic Formula
A = P(1 + r)^t
Where:
- A = final amount
- P = principal (starting amount)
- r = rate of return (as a decimal)
- t = time (in years)
Adding Regular Contributions
When you make regular contributions, the formula becomes:
FV = P(1 + r)^t + PMT × [((1 + r)^t – 1) / r]
Where:
- FV = future value
- P = initial investment
- PMT = regular payment amount
- r = periodic interest rate
- t = number of periods
Don’t worry if this looks complicated; you don’t need to calculate it manually. Online calculators and spreadsheets handle the math for you.
The Natural Exponential Constant (e)
In continuous compounding (which is theoretical but useful for understanding), growth uses the constant e (approximately 2.71828).
The formula becomes: A = Pe^(rt)
This represents the mathematical limit of compounding—what happens when interest compounds infinitely often. While not practical for most investments, it helps illustrate that more frequent compounding (daily vs. monthly vs. annually) does increase returns slightly.
💰 Exponential Growth Calculator
See the power of compound interest and exponential growth in action
Conclusion: Harness the Power of Exponential Growth Today
Exponential growth is the closest thing to magic in the world of investing—but it’s not actually magic. It’s mathematics, patience, and consistency working together to transform modest contributions into substantial wealth over time.
The key insights to remember:
Time is your most valuable asset—every year you delay costs you multiple years of growth on the back end
Small differences compound dramatically—a 2% higher return or starting 5 years earlier can mean hundreds of thousands of dollars
Consistency beats perfection—regular contributions and staying invested matter more than trying to time the market
Reinvesting accelerates growth—dividends and returns that stay invested create exponential acceleration
Patience is required—the J-curve means growth feels slow at first but becomes explosive later
Your Next Steps
1. Start immediately (if you haven’t already)
Open a retirement account and make your first contribution today. Even $50/month starting now beats $500/month starting in five years.
2. Automate your contributions
Set up automatic transfers so you never miss a contribution. Consistency is exponential growth’s best friend.
3. Maximize tax-advantaged accounts
Prioritize 401(k)s, IRAs, and Roth accounts to keep more money compounding tax-free or tax-deferred.
4. Reinvest all dividends
Configure your accounts to automatically reinvest dividends and distributions.
5. Increase contributions annually
Commit to raising your contribution rate by 1-2% each year as your income grows.
6. Stay invested through volatility
Understand the cycle of market emotions and resist the urge to sell during downturns.
7. Educate yourself continuously
Keep learning about the stock market and investment strategies through resources like TheRichGuyMath blog.
Remember: The best time to plant a tree was 20 years ago. The second-best time is today. The same principle applies to harnessing exponential growth for your financial future.
Warren Buffett didn’t become one of the world’s wealthiest people by making dramatically different investments than other successful investors—he simply started early and let exponential growth work for six decades. You have the same tool available to you.
The power of exponential growth is real, accessible, and waiting for you to put it to work. The only question is: will you start today, or will you look back in 10, 20, or 30 years wishing you had?
FAQ: Exponential Growth
A good exponential growth rate depends on your asset allocation and risk tolerance. Historically, the stock market has returned approximately 10% annually before inflation (about 7% after inflation). Conservative portfolios with bonds might target 6-8%, while aggressive growth portfolios might aim for 10-12%. Remember that higher returns typically come with higher volatility and risk.
Use the formula: Final Value = Initial Investment × (1 + Annual Return)^Number of Years. For example, $10,000 invested at 8% for 20 years equals $10,000 × (1.08)^20 = $46,610. For regular contributions, use a compound interest calculator or spreadsheet that accounts for periodic deposits.
Compound interest is a specific application of exponential growth. Exponential growth is the broader mathematical concept where something increases by a fixed percentage over time. Compound interest is exponential growth applied to financial investments—earning returns on your returns creates the exponential pattern.
In mathematics, exponential functions continue indefinitely. In real-world investing, exponential growth faces practical limits—economic cycles, market corrections, inflation, and changing circumstances. However, over multi-decade periods, diversified market investments have historically demonstrated exponential growth patterns despite temporary setbacks.
Exponential growth appears slow initially because you’re earning returns on a small base. A 10% return on $1,000 is only $100. But as your balance grows, those same percentage returns represent larger dollar amounts. Eventually, you reach a tipping point where annual growth exceeds your contributions—that’s when exponential growth becomes visibly dramatic.
Inflation reduces the real (inflation-adjusted) growth rate. If your investments grow at 8% annually but inflation is 3%, your real growth rate is approximately 5%. This is why it’s crucial to invest in assets that can outpace inflation—otherwise, your purchasing power declines even as your nominal account balance grows.
The biggest threats are: (1) starting too late, (2) interrupting contributions or withdrawing early, (3) panic-selling during market downturns, (4) paying excessive fees, and (5) taking on inappropriate risk that leads to devastating losses. Consistency and patience are exponential growth’s best friends; impulsive decisions are its worst enemies.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Investing involves risk, including the potential loss of principal. Past performance does not guarantee future results. The historical returns and examples cited are for illustrative purposes and may not reflect actual future performance. Always consult with a qualified financial advisor before making investment decisions based on your individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and financial goals.
About the Author
Written by Max Fonji — With over a decade of experience in financial education and investment strategy, Max is your go-to source for clear, data-backed investing education. Through TheRichGuyMath.com, Max helps everyday investors understand complex financial concepts and build wealth through proven, time-tested strategies. Max believes that financial literacy is the foundation of wealth building and that anyone, regardless of their starting point, can achieve financial independence through education, discipline, and the power of exponential growth.