Ever looked at a company’s financial statements and wondered what those big numbers really mean? You’re not alone. When you’re trying to understand whether a business is actually making money, or just moving it around net revenue is one of the first metrics you need to master. Unlike those flashy “total sales” numbers companies love to brag about, net revenue tells you what the business actually keeps after all the returns, discounts, and allowances. Think of it as the difference between what a store rings up at the register versus what ends up in the bank after customers return items and apply coupons. For anyone serious about investing, understanding net revenue isn’t optional—it’s essential.
TL;DR
- Net revenue is the actual income a company retains after subtracting returns, allowances, and discounts from gross revenue; it’s the “real” top-line number
- The formula is simple: Net Revenue = Gross Revenue – (Returns + Allowances + Discounts)
- Net revenue matters more than gross revenue because it shows what money a business truly earns and can use for operations and growth
- Investors use net revenue to evaluate company health, compare businesses accurately, and make informed decisions about stock market investments
- A company can have high gross revenue but poor net revenue if it offers excessive discounts or experiences high return rates—always look beyond the headline number
What Is Net Revenue? The Complete Definition
In simple terms, net revenue means the total amount of money a company actually earns from sales after accounting for all the deductions that reduce the initial sale amount.
When a business sells products or services, it doesn’t get to keep every dollar that shows up on the receipt. Customers return items, companies offer promotional discounts, and sometimes they provide allowances for damaged goods. Net revenue represents what’s left after all these adjustments—the true income a company brings in.
Net revenue is also called “net sales” or “revenue net of returns and allowances.” It appears at the very top of the income statement, which is why finance professionals often call it the “top line” number (as opposed to “bottom line” profit).
Here’s why it matters: A company might report $10 million in gross sales, but if $2 million comes back as returns and discounts, the business only actually earned $8 million. That $8 million—the net revenue—is what the company has available to cover costs, pay employees, and hopefully generate profit.
The Net Revenue Formula Explained
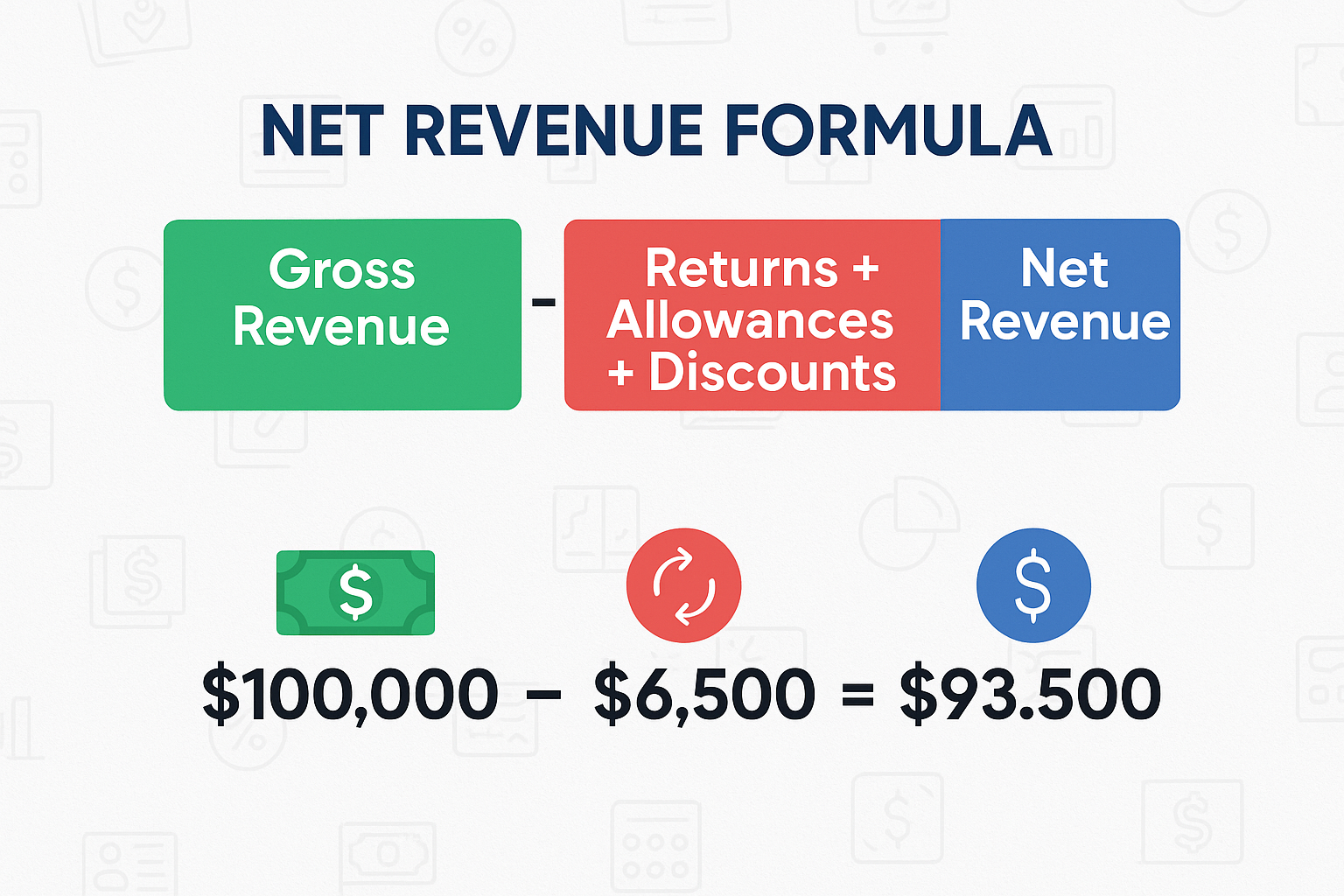
The formula for calculating net revenue is straightforward:
Net Revenue = Gross Revenue – (Returns + Allowances + Discounts)
Let’s break down each component:
Gross Revenue
This is the total dollar amount of all sales before any deductions. If you sold 1,000 products at $100 each, your gross revenue is $100,000. Simple multiplication.
Returns
Money refunded to customers who send products back. If 50 customers returned their $100 products, that’s $5,000 in returns.
Allowances
Price reductions given after the sale, often for damaged or defective goods that customers keep anyway. If you gave 20 customers a $25 credit for slightly damaged items, that’s $500 in allowances.
Discounts
Price reductions offered at the time of sale—think promotional codes, bulk discounts, or early payment incentives. If 100 customers used a 10% off coupon ($10 each), that’s $1,000 in discounts.
Example Calculation:
- Gross Revenue: $100,000
- Returns: $5,000
- Allowances: $500
- Discounts: $1,000
- Net Revenue = $100,000 – ($5,000 + $500 + $1,000) = $93,500
The company’s actual earnings from sales is $93,500, not $100,000. That $6,500 difference can significantly impact profitability analysis.
Net Revenue vs Gross Revenue: What’s the Difference?
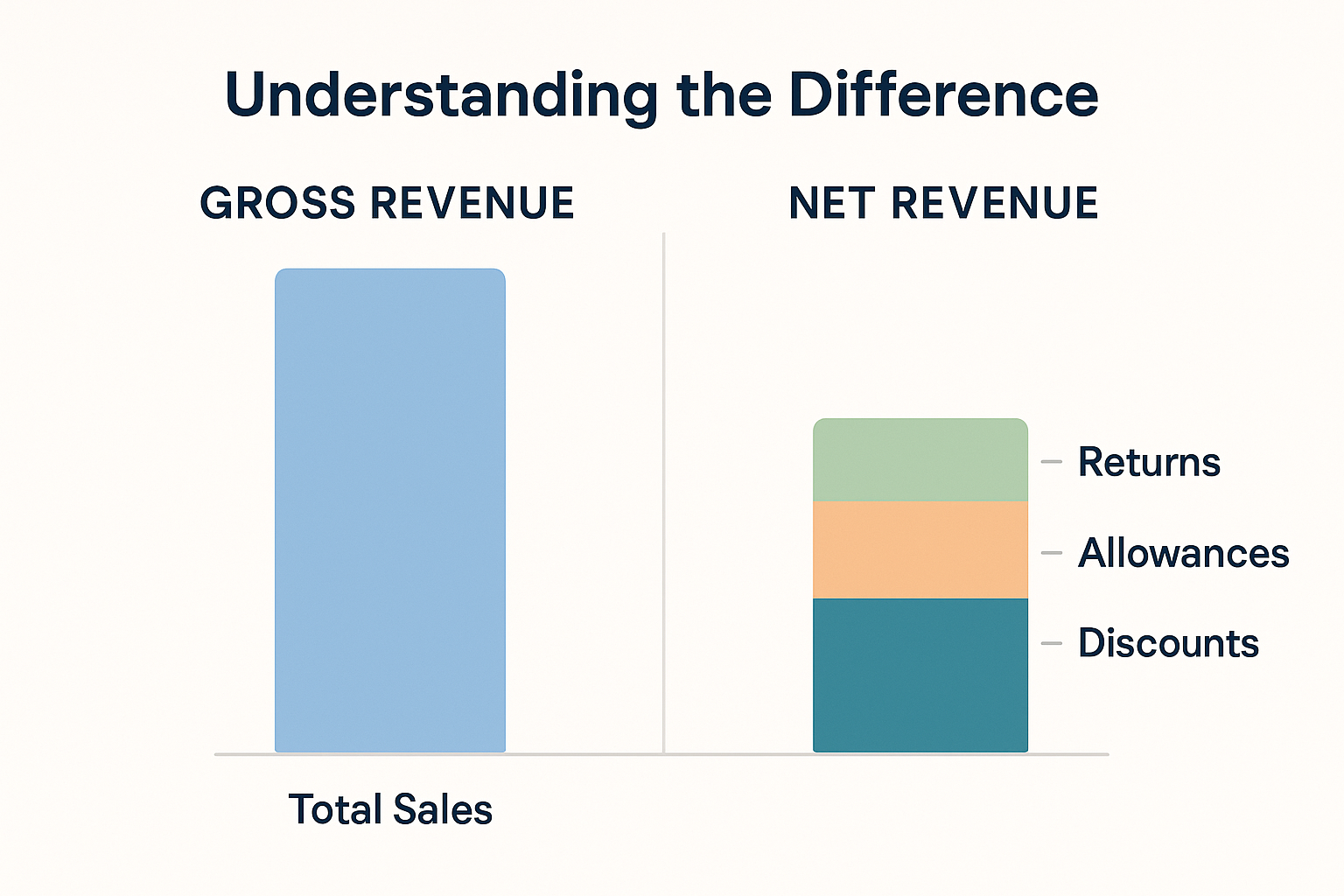
Many beginners confuse these two terms, but understanding the distinction is crucial for evaluating any business.
| Metric | Definition | What It Shows | Where It Appears |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Revenue | Total sales before any deductions | Maximum potential income | Initial sales reports |
| Net Revenue | Sales after returns, discounts, and allowances | Actual income retained | Top of income statement |
Gross revenue is like counting all the money that went into the cash register. Net revenue is what you actually get to deposit in the bank after handling refunds and honoring discounts.
Why This Matters for Investors
When you’re researching companies for dividend investing or evaluating high dividend stocks, you want to know the real revenue picture. A company might boast impressive gross sales, but if they’re constantly discounting products or dealing with massive returns, their net revenue tells a different story.
Real-world example: An e-commerce retailer reports $50 million in gross revenue during the holiday season. Sounds impressive! But after accounting for post-holiday returns (20%), promotional discounts (15%), and allowances for shipping damage (2%), the net revenue drops to approximately $31.5 million. That’s a 37% reduction—and it completely changes the company’s profitability outlook.
How to Calculate Net Revenue: Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s walk through a practical example using a fictional company called “TechGadgets Inc.”
Step 1: Identify Gross Revenue
TechGadgets sold 5,000 smartphones at $800 each during Q1 2025.
- Gross Revenue = 5,000 × $800 = $4,000,000
Step 2: Calculate Returns
200 customers returned their phones for full refunds.
- Returns = 200 × $800 = $160,000
Step 3: Calculate Allowances
100 customers received a $50 credit for minor screen defects, but kept the phones.
- Allowances = 100 × $50 = $5,000
Step 4: Calculate Discounts
500 customers used a promotional code for $80 off.
- Discounts = 500 × $80 = $40,000
Step 5: Apply the Formula
Net Revenue = $4,000,000 – ($160,000 + $5,000 + $40,000)
Net Revenue = $4,000,000 – $205,000
Net Revenue = $3,795,000
TechGadgets’ actual revenue for Q1 2025 is $3,795,000—about 5% less than the gross figure. This is the number analysts use to evaluate the company’s true performance.
Why Net Revenue Matters: The Investor’s Perspective
Understanding net revenue isn’t just an accounting exercise—it directly impacts your investment decisions and portfolio performance.
1. Accurate Company Valuation
When you’re analyzing potential investments, net revenue provides the foundation for calculating important metrics like:
- Price-to-Sales (P/S) ratio
- Revenue growth rate
- Profit margins
Using gross revenue instead of net revenue inflates these metrics, making a company look more valuable than it actually is.
2. Reveals Business Quality
The gap between gross and net revenue tells you a lot about a company’s operational health:
- Small gap (1-5%): Healthy business with quality products and satisfied customers
- Medium gap (5-15%): Normal for competitive industries with regular promotions
- Large gap (15%+): Potential red flag—excessive discounting or quality issues
3. Trend Analysis Over Time
Tracking net revenue across quarters and years helps you spot important patterns:
- Widening gap: The Company may be struggling with competition, forcing deeper discounts
- Narrowing gap: Improving product quality or brand strength, reducing returns
- Consistent gap: Stable, predictable business model
4. Industry Comparison
Net revenue allows apples-to-apples comparisons between companies. Two retailers might both report $1 billion in gross sales, but if one has $900 million in net revenue and the other has $750 million, you’re looking at very different businesses.
For those exploring passive income strategies, companies with strong, growing net revenue tend to be more reliable dividend payers and better long-term investments.
Net Revenue vs Net Income: Don’t Get Confused!
Here’s where many beginners stumble: net revenue and net income sound similar but represent completely different things.
Net Revenue:
- Top of the income statement
- Revenue after sales-related deductions (returns, discounts, allowances)
- Doesn’t account for operating expenses, taxes, or other costs
- Shows what the company earned from sales activities
Net Income:
- Bottom of the income statement (the “bottom line”)
- Profit after all expenses, including operating costs, interest, taxes, and depreciation
- Shows what the company actually gets to keep
- The final measure of profitability
Think of it this way: Net revenue is what you earn. Net income is what you keep after paying all your bills.
Example:
- Net Revenue: $1,000,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $400,000
- Operating Expenses: $300,000
- Interest & Taxes: $100,000
- Net Income: $200,000
Both metrics matter, but they answer different questions. Net revenue tells you about sales performance; net income tells you about overall profitability.
Common Mistakes When Analyzing Net Revenue
Even experienced investors sometimes make these errors when evaluating net revenue:
Mistake #1: Ignoring Industry Context
A 10% gap between gross and net revenue might be excellent in retail (where returns are common), but concerning in software (where returns should be rare). Always compare companies within the same industry.
Mistake #2: Focusing Only on Growth Rate
A company showing 50% net revenue growth sounds amazing—until you realize it’s coming from unsustainable discounting that’s destroying profit margins. Look at how revenue is growing, not just that it’s growing.
Mistake #3: Not Reading the Fine Print
Companies sometimes change how they report revenue, especially around new accounting standards. Always check the footnotes in financial statements for methodology changes that might affect year-over-year comparisons.
Mistake #4: Treating All Deductions Equally
A company with high returns might have quality problems. A company with high discounts might face intense competition. A company with high allowances might have shipping issues. Each deduction type tells a different story about the business.
Mistake #5: Overlooking Seasonality
Many businesses have seasonal patterns. Comparing Q4 (holiday season) net revenue to Q1 might show a decline that’s normal. Always compare the same quarters year-over-year.
💰 Net Revenue Calculator
Calculate your actual revenue after deductions
How Companies Report Net Revenue: Real-World Examples
Understanding how actual companies report net revenue helps you apply these concepts when analyzing investments.
Example 1: Apple Inc.
Apple’s 2024 annual report shows:
- Product Revenue (Gross): $298 billion
- Deductions: Estimated $8-12 billion (returns, allowances, incentives)
- Product Revenue (Net): Approximately $286-290 billion
Apple’s deduction rate is relatively low (3-4%) because of strong brand loyalty, quality products, and a robust ecosystem that reduces returns.
Example 2: Amazon
Amazon’s retail operations show:
- Gross Merchandise Value: Much higher than reported revenue
- Net Revenue: Reflects actual sales after returns and marketplace fees
- Deduction Rate: Higher than Apple (8-12%) due to the nature of e-commerce and third-party sales
Amazon’s business model includes significant returns (especially in apparel and electronics), which creates a larger gap between gross and net figures.
Example 3: Traditional Retail
A typical department store might show:
- Gross Sales: $500 million
- Returns: $75 million (15%)
- Promotional Discounts: $50 million (10%)
- Allowances: $10 million (2%)
- Net Revenue: $365 million (73% retention)
This 27% reduction is common in traditional retail, where seasonal sales, returns, and competitive pricing create substantial deductions.
Net Revenue in Different Industries: What’s Normal?
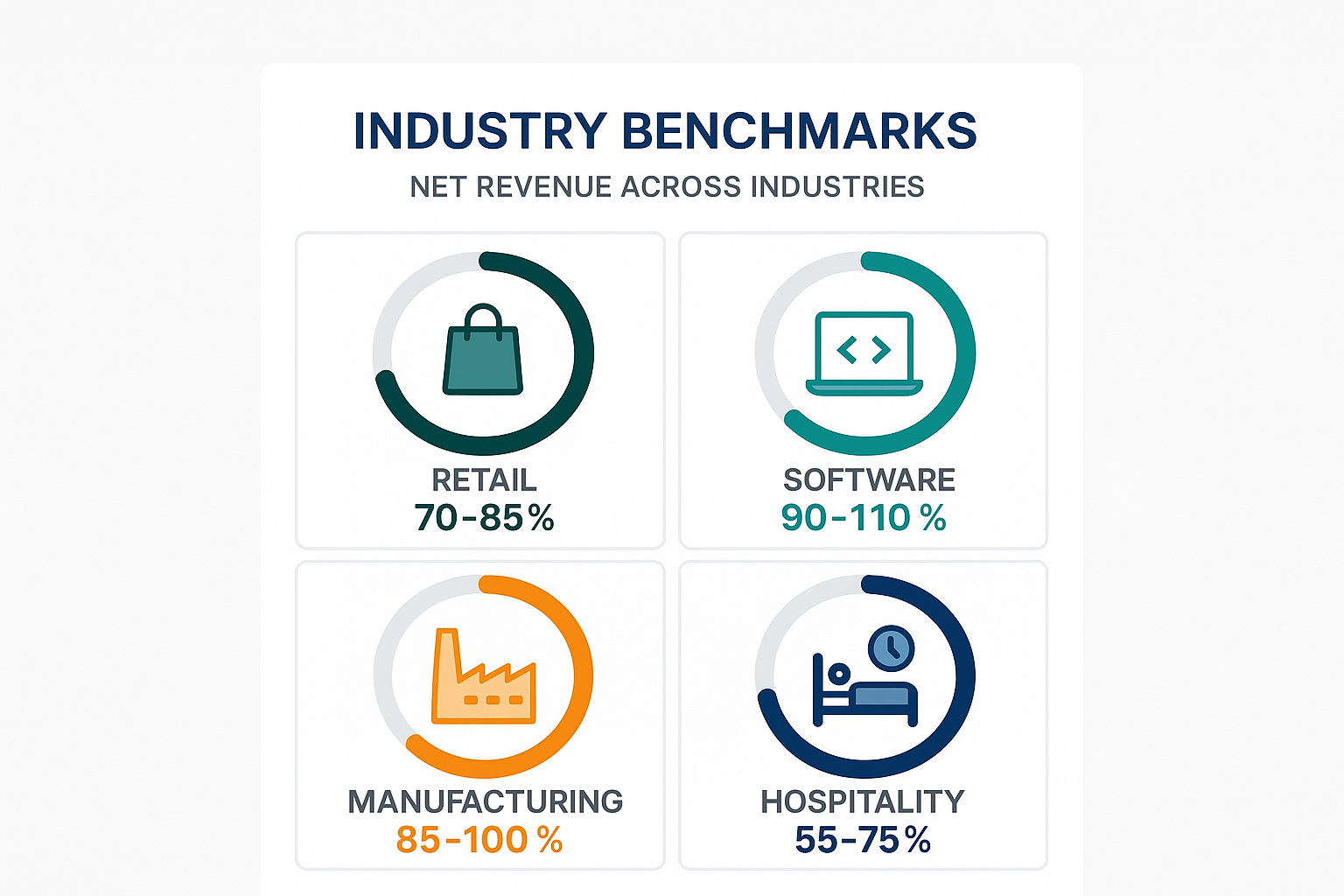
The “healthy” gap between gross and net revenue varies significantly by industry. Here’s what to expect:
Retail & E-commerce
- Typical Net Revenue: 70-85% of gross
- Main Deductions: Returns (10-30%), promotional discounts (5-15%)
- Red Flags: Retention below 70% suggests quality or pricing issues
Software & SaaS
- Typical Net Revenue: 90-98% of gross
- Main Deductions: Refunds (rare), early cancellations, volume discounts
- Red Flags: Increasing refund rates may indicate product-market fit problems
Manufacturing
- Typical Net Revenue: 85-95% of gross
- Main Deductions: Volume discounts, early payment discounts, defect allowances
- Red Flags: Rising allowances suggest quality control issues
Hospitality & Services
- Typical Net Revenue: 80-90% of gross
- Main Deductions: Cancellations, promotional rates, loyalty program redemptions
- Red Flags: Heavy discounting to maintain occupancy/utilization
When evaluating companies in the stock market, always compare net revenue retention rates to industry benchmarks, not absolute standards.
Using Net Revenue for Investment Decisions
Now that you understand what net revenue is and how it’s calculated, let’s explore how to use this metric when making investment choices.
Screening for Quality Companies
Step 1: Check the Trend
Look for companies with stable or improving net revenue over 3-5 years. Consistent growth indicates:
- Strong product-market fit
- Effective pricing strategies
- Healthy customer relationships
Step 2: Compare to Competitors
Within the same industry, companies with higher net revenue retention typically have:
- Better brand strength
- Superior product quality
- More loyal customer bases
Step 3: Calculate Revenue Quality Score
Create a simple metric: (Net Revenue / Gross Revenue) × 100
- Above 95%: Exceptional quality
- 90-95%: Very good
- 85-90%: Good
- 80-85%: Acceptable
- Below 80%: Investigate further
Red Flags to Watch For
Declining Net Revenue with Stable Gross Revenue
This pattern suggests the company is:
- Offering deeper discounts to maintain sales volume
- Experiencing higher return rates
- Facing increased competition
Volatile Quarter-to-Quarter Changes
While some seasonality is normal, wild swings in net revenue retention may indicate:
- Inconsistent pricing strategies
- Quality control problems
- Aggressive promotional tactics
Industry-Lagging Performance
If a company’s net revenue retention is significantly below industry peers, dig deeper into:
- Product reviews and customer satisfaction
- Competitive positioning
- Management commentary on pricing and returns
For investors focused on dividend stocks, strong net revenue is particularly important—it’s the foundation that supports sustainable dividend payments.
Net Revenue and Profitability: The Connection
While net revenue and profitability are different metrics, they’re intimately connected. Here’s how:
The Profitability Chain
Net Revenue (what you earn from sales)
↓
Minus: Cost of Goods Sold (what products/services cost to deliver)
↓
Equals: Gross Profit (initial profitability)
↓
Minus: Operating Expenses (salaries, rent, marketing, etc.)
↓
Equals: Operating Income (core business profitability)
↓
Minus: Interest, Taxes, Other (financial and tax obligations)
↓
Equals: Net Income (final bottom-line profit)
Key insight: If net revenue is inflated or declining, every metric down the chain is affected. You can’t have sustainable profitability without healthy net revenue.
Margin Analysis
Smart investors look at how net revenue translates into profit:
Gross Profit Margin = (Net Revenue – COGS) / Net Revenue
Two companies with identical net revenue can have vastly different profitability depending on their cost structures. But the starting point—accurate net revenue—is essential for meaningful margin analysis.
Growth vs Quality Trade-off
Some companies sacrifice net revenue quality for growth:
- Offering unsustainable discounts to acquire customers
- Accepting high return rates to boost gross sales
- Providing generous allowances to close deals
This strategy can work temporarily, but often leads to profitability problems. When evaluating growth companies, always ask: “Is this revenue growth sustainable, or is it built on discounting and allowances that will eventually hurt margins?”
Understanding these dynamics helps you make smarter decisions about what moves the stock market and which companies are positioned for long-term success.
How to Find Net Revenue Information
Ready to analyze real companies? Here’s where to find net revenue data:
Company Financial Statements
Income Statement (Statement of Operations)
- Look for the very first line item
- May be labeled “Net Sales,” “Net Revenue,” or “Revenue”
- Some companies show gross revenue with deductions itemized below
SEC Filings (U.S. Public Companies)
- 10-K: Annual report with complete financial statements
- 10-Q: Quarterly report with interim financial data
- Available free at SEC.gov
Financial Data Platforms
Free Resources:
- Yahoo Finance: Basic financials for most public companies
- Google Finance: Quick revenue snapshots
- Company investor relations websites: Often, the most up-to-date information
Premium Resources:
- Morningstar: Detailed financial analysis and historical data
- Bloomberg Terminal: Professional-grade data (expensive)
- FactSet: Institutional research platform
Reading the Fine Print
Always check the Notes to Financial Statements section. Companies must disclose:
- Revenue recognition policies
- Significant changes in accounting methods
- Unusual items affecting revenue
- Segment breakdowns (if the company operates multiple businesses)
This information provides crucial context for interpreting net revenue figures and understanding trends.
Advanced Concepts: Revenue Recognition and Timing
As you become more sophisticated in your analysis, understanding when companies recognize revenue becomes important.
Revenue Recognition Standards
In 2018, new accounting rules (ASC 606 in the U.S., IFRS 15 internationally) changed how companies recognize revenue. The core principle: recognize revenue when control of goods/services transfers to the customer, not necessarily when cash changes hands.
This matters because:
- Some companies recognize revenue before receiving payment
- Returns and allowances might be estimated rather than actual
- Timing differences can create volatility in reported net revenue
Deferred Revenue vs. Net Revenue
Deferred revenue (also called “unearned revenue”) is money received but not yet earned—like subscription payments for future services. This appears as a liability on the balance sheet, not as net revenue.
Example: A software company receives $1,200 for an annual subscription in January. They don’t record $1,200 in net revenue immediately. Instead, they recognize $100 per month over 12 months as they deliver the service.
Understanding these timing issues helps you avoid misinterpreting revenue trends, especially in subscription-based businesses.
Practical Tips for Beginner Investors
Ready to put this knowledge into action? Here are actionable steps for incorporating net revenue analysis into your investment process:
Create a Simple Checklist
When evaluating any company, ask:
- What’s the net revenue for the most recent quarter/year?
- How does it compare to the same period last year?
- What’s the trend over the past 3-5 years?
- How does net revenue retention compare to industry peers?
- Are there any unusual items or accounting changes affecting the numbers?
Build a Comparison Spreadsheet
Track 3-5 companies in the same industry with columns for:
- Gross revenue
- Net revenue
- Retention percentage (Net/Gross)
- Year-over-year growth
- Quarterly trends
This side-by-side comparison quickly reveals which companies have the strongest revenue quality.
Keep Learning
Net revenue is just one piece of the puzzle. Expand your knowledge by exploring:
- What is investing fundamentals
- Market volatility and how revenue affects it
- Smart investment moves for building wealth
Start Small
Don’t try to analyze every company at once. Pick one or two businesses you understand well (companies whose products you use), find their financial statements, and practice identifying and interpreting their net revenue. As you get comfortable, expand to new industries and more complex businesses.
Review Regularly
Revenue quality can change over time. Set a reminder to review your holdings quarterly when companies release earnings reports. Look for:
- Changes in net revenue trends
- Management commentary on returns, discounts, or pricing
- Shifts in competitive dynamics affecting revenue quality
The Bigger Picture: Net Revenue in Your Investment Strategy
Understanding net revenue isn’t just about analyzing individual companies—it’s about building a comprehensive, informed investment approach.
Building a Quality-Focused Portfolio
Investors who prioritize companies with strong, consistent net revenue tend to build more resilient portfolios. These businesses typically:
- Weather economic downturns better
- Maintain pricing power during inflation
- Generate sustainable cash flows for dividends and reinvestment
- Compound wealth more reliably over time
This quality-first approach aligns perfectly with strategies like dividend investing, where consistent revenue supports consistent payouts.
Avoiding Value Traps
Some stocks look cheap based on traditional metrics like P/E ratios, but deteriorating net revenue reveals the real problem. A company might trade at 8x earnings, but if net revenue is declining because of:
- Increasing competitive pressure requires heavy discounting
- Quality issues are driving high return rates
- Loss of pricing power in the market
…then that “cheap” stock is actually a value trap. Net revenue analysis helps you distinguish genuine bargains from troubled businesses.
Complementing Other Metrics
Net revenue works best when combined with other analytical tools:
- Cash flow analysis: Does net revenue convert to actual cash?
- Margin trends: Is the company maintaining profitability as revenue grows?
- Balance sheet health: Can the company sustain operations if revenue temporarily declines?
- Competitive positioning: Why is this company’s revenue quality better or worse than its peers?
The most successful investors don’t rely on any single metric—they build a comprehensive understanding using multiple perspectives.
Common Scenarios: Interpreting Net Revenue Patterns
Let’s look at some real-world patterns you might encounter and what they mean:
Scenario 1: Growing Gross Revenue, Declining Net Revenue
What it looks like: Gross sales up 20%, but net revenue only up 5%
What it means: The company is likely:
- Offering deeper discounts to drive volume
- Experiencing higher return rates
- Facing pricing pressure from competitors
Action: Investigate further. Read earnings call transcripts for management’s explanation. This pattern often precedes margin compression and profit warnings.
Scenario 2: Stable Net Revenue, Declining Gross Revenue
What it looks like: Gross sales down 10%, but net revenue only down 2%
What it means: The company might be:
- Reducing promotional activity and focusing on full-price sales
- Improving product quality, leading to fewer returns
- Shifting to higher-value customers
Action: Potentially positive. Check if operating margins are improving, which would confirm this is a quality-enhancing strategy.
Scenario 3: Both Growing Consistently
What it looks like: Gross revenue up 15%, net revenue up 14%
What it means: Healthy, sustainable growth with:
- Consistent pricing strategies
- Stable product quality
- Strong market position
Action: This is what you want to see. Verify the trend continues over multiple quarters and compare to industry growth rates.
Scenario 4: Volatile Quarter-to-Quarter
What it looks like: Net revenue retention swings between 75% and 92% across quarters
What it means: Possible issues:
- Heavy reliance on promotional periods
- Seasonal business without proper adjustment
- Inconsistent operational execution
Action: Look at year-over-year same-quarter comparisons rather than sequential quarters. If volatility persists even in year-over-year data, it’s a red flag.
Tools and Resources for Deeper Analysis
Want to take your net revenue analysis to the next level? Here are valuable resources:
Educational Resources
SEC’s Guide to Financial Statements
Free resource explaining how to read and interpret corporate financial reports, including revenue recognition.
Investopedia’s Financial Analysis Section
Comprehensive articles on financial metrics, ratios, and analysis techniques.
CFA Institute Publications
Professional-level insights into financial analysis and investment decision-making. Analysis Tools
Excel/Google Sheets Templates
Create your own financial models tracking net revenue trends, growth rates, and peer comparisons.
Screening Tools
Platforms like Finviz, Stock Rover, or Seeking Alpha allow you to filter companies by revenue growth and other financial criteria.
Company Presentations
Most companies publish quarterly earnings presentations on their investor relations websites, often with helpful revenue breakdowns and explanations.
Recommended Reading
For those serious about mastering financial analysis and investing fundamentals, consider these classic resources:
- “Financial Statements” by Thomas Ittelson – Visual guide to understanding financial reports
- “The Interpretation of Financial Statements” by Benjamin Graham – Classic value investing perspective
- Annual reports from companies you admire – Real-world practice with actual data
Conclusion: Making Net Revenue Work for You
Net revenue isn’t just an accounting term buried in financial statements—it’s a powerful tool that helps you see through the marketing hype and understand what businesses are really earning.
The key takeaways to remember:
- Net revenue shows actual income after returns, discounts, and allowances—it’s more meaningful than gross sales figures
- The formula is simple: Gross Revenue – (Returns + Allowances + Discounts) = Net Revenue
- Quality matters as much as quantity—a company retaining 95% of gross revenue is fundamentally stronger than one retaining 70%
- Context is critical—always compare companies within the same industry and examine trends over time
- Net revenue is the foundation for all downstream profitability metrics and investment analysis
Your Next Steps
This week:
- Choose one company you’re interested in (or already own)
- Find their latest 10-K or 10-Q filing on SEC.gov
- Locate the net revenue figure on the income statement
- Calculate the retention percentage and compare it to the previous year
This month:
- Build a simple spreadsheet comparing 3-5 companies in the same industry
- Track their net revenue trends over the past 3 years
- Identify which companies show the strongest revenue quality
This quarter:
- Incorporate net revenue analysis into your regular investment research process
- Review your existing holdings to ensure they maintain healthy revenue quality
- Explore additional financial metrics to complement your net revenue knowledge
Remember, successful investing isn’t about finding a magic formula—it’s about building a solid foundation of understanding. Net revenue analysis is one essential brick in that foundation.
As you continue your investment journey, keep exploring resources on smart investing strategies and building passive income. The more you learn, the better equipped you’ll be to make confident, informed decisions with your money.
The companies with the strongest net revenue today often become the wealth-building investments of tomorrow. Now you have the tools to identify them.
FAQ: Net Revenue
A “good” net revenue percentage depends entirely on the industry. Software companies should retain 90-98% of gross revenue, while traditional retailers might only keep 70-85%. Compare companies within the same sector, and look for stable or improving trends rather than absolute benchmarks.
The formula for net revenue is: Gross Revenue – (Returns + Allowances + Discounts) = Net Revenue. Start with total sales, then subtract all customer refunds, price adjustments for defects, and promotional discounts to find the actual amount the company retains.
No, net revenue and profit are completely different. Net revenue (also called net sales) is income from sales after deductions like returns and discounts. Profit (net income) is what remains after subtracting all expenses, including costs of goods sold, operating expenses, interest, and taxes. Net revenue is the “top line,” while profit is the “bottom line.”
Net revenue shows the actual income a company generates from sales, providing a more accurate picture than gross revenue. Investors use net revenue to calculate valuation ratios, assess revenue quality, identify business problems (like excessive discounting or high returns), and make informed decisions about stock investments.
Technically, yes—if returns, allowances, and discounts exceed gross sales, net revenue would be negative. However, this is extremely rare and would indicate a severe business crisis. More commonly, you might see negative revenue growth (net revenue declining compared to previous periods), which signals business challenges.
Net revenue appears at the very top of the income statement (statement of operations). It’s the first line item, which is why it’s called the “top line” number. Some companies label it “Net Sales,” “Revenue,” or “Net Revenue.”
Net revenue directly impacts stock prices because it’s the foundation for profitability and growth. Strong, growing net revenue typically supports higher stock valuations, while declining or poor-quality net revenue often leads to price declines. Understanding why the stock market goes up requires understanding the revenue that drives corporate earnings.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Net revenue analysis is one component of comprehensive investment research and should not be the sole basis for investment decisions. Always conduct thorough due diligence, consider your individual financial situation and risk tolerance, and consult with qualified financial professionals before making investment decisions. Past performance of companies’ net revenue does not guarantee future results. The author and publisher are not responsible for any investment decisions made based on the information in this article.
About the Author
Written by Max Fonji — With over a decade of experience in financial analysis and investment education, Max is your go-to source for clear, data-backed investing insights. Through TheRichGuyMath.com, Max helps everyday investors build wealth through understanding fundamental financial concepts and making informed decisions. When not analyzing financial statements, Max is passionate about making complex investing topics accessible to beginners and experienced investors alike.