Whether you’re a beginner investor or a seasoned market watcher, chances are you’ve heard of the S&P 500. It’s not just another financial acronym—it’s one of the most important indicators of the U.S. economy. Representing 500 of the largest publicly traded companies, the S&P 500 acts as a mirror reflecting America’s corporate health, investor sentiment, and long-term growth potential.
In this guide, you’ll discover exactly what the S&P 500 is, how it works, and why it plays a crucial role in shaping investment decisions globally. By the end, you’ll know how to leverage it for smarter, more diversified investments—whether through ETFs, index funds, or automated platforms.
Let’s break it all down in simple terms—with data, charts, and real-world examples.
What Is the S&P 500?
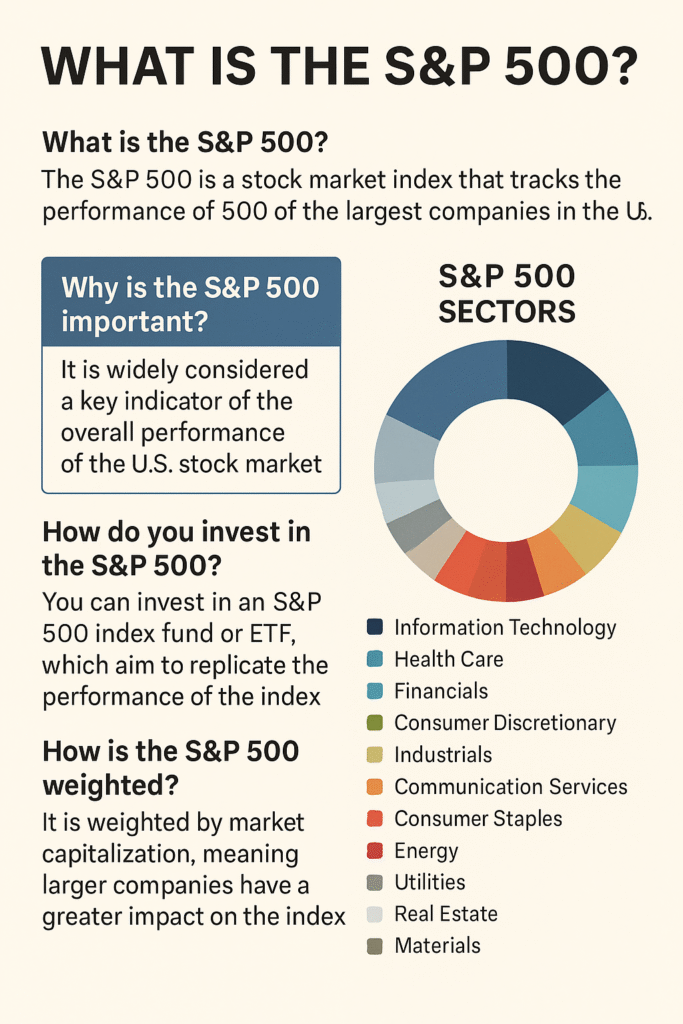
The S&P 500, short for Standard & Poor’s 500, is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the U.S. It serves as a benchmark for the overall U.S. stock market and is used by investors to measure the health of the economy.
Think of it as the DNA of the U.S. economy—covering tech, healthcare, energy, finance, and more.
How Does the S&P 500 Work?
The index is market-cap weighted, meaning larger companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon have more influence than smaller ones.
To qualify for the index, a company must:
- Be U.S.-based
- Have a market cap of at least $14.5 billion (as of 2024)
- Be highly liquid (actively traded)
- Have positive earnings in recent quarters
The index is updated quarterly by a committee to ensure it remains representative.
What Companies Are in the S&P 500?
It includes giants such as:
- Apple (AAPL)
- Microsoft (MSFT)
- Nvidia (NVDA)
- Amazon (AMZN)
- Berkshire Hathaway (BRK.B)
A full, real-time list is available at S&P Global or most brokerage platforms.
Why Is the S&P 500 Important?
- Broad Exposure: It covers ~80% of the total U.S. equity market.
- Historical Growth: A reliable performer over long periods.
- Benchmark Standard: Mutual funds, ETFs, and even robo-advisors benchmark against it.
Many consider it the best representation of the U.S. stock market.
Historical Performance of the SP 500
| Time Period | Average Annual Return |
|---|---|
| Last 5 Years | ~12.3% |
| Last 10 Years | ~11.5% |
| Since Inception (1957) | ~10.5% |
If you had invested $10,000 in the S&P 500 in 2000, it would be worth over $56,000 by 2025.
How to Invest in the S&P 500
You can invest via:
- ETFs like SPDR S&P500 ETF Trust (SPY), Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO)
- Mutual funds that mirror the index
- Robo-advisors like Betterment or Wealthfront
Minimum to start: As low as $1 with fractional shares!
S&P 500 vs Other Indexes
| Feature | S&P 500 | NASDAQ | Dow Jones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Large-cap U.S. | Tech-heavy | 30 major firms |
| # of Companies | 500 | ~3,300 | 30 |
| Weighting Method | Market-cap | Market-cap | Price-weighted |
Future Outlook:
Despite short-term volatility, experts believe the S&P500 will continue its upward trend due to:
- Strong corporate earnings
- AI and tech innovation
- Global economic resilience
Many projections estimate an average 7–10% annual return over the next 20 years.
Yes, short-term losses are possible during market downturns, but long-term trends are generally upward.
Absolutely. It offers instant diversification with just one investment.
It’s rebalanced quarterly, but only a few companies change each year.
Final Thoughts:
If you’re looking for long-term growth, low fees, and a proven track record, the S&P 500 is one of the best investment options available. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned investor, it deserves a place in your portfolio.