Dividend investing is an investment strategy focused on buying stocks or funds that pay dividends, regular payments made by companies or other entities to shareholders.
Imagine opening your bank account each month to find fresh deposits, money you didn’t have to trade hours for, money that arrived while you were sleeping, traveling, or spending time with loved ones. This isn’t a fantasy; it’s the reality for millions of dividend investors who’ve built portfolios that pay them regularly, just for owning shares in quality companies.
Dividend investing represents one of the most accessible and time-tested wealth-building strategies available to everyday investors. Unlike the adrenaline-fueled world of day trading or the complexity of options strategies, dividend investing offers something refreshingly straightforward: own pieces of profitable businesses, and they’ll share their success with you through regular cash payments. Investopedia: definitions, investing basics
Whether you’re a complete beginner taking your first steps into the stock market or an experienced investor looking to refine your strategy, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about building a dividend portfolio that generates reliable income for years to come.
Key Takeaways

- Dividend investing provides regular passive income through cash payments from profitable companies, creating a reliable income stream without selling shares
- Reinvesting dividends through compounding can dramatically accelerate wealth accumulation, with dividend reinvestment historically contributing 40% of total stock market returns
- Successful dividend portfolios balance yield, growth, and safety by focusing on dividend aristocrats, reasonable payout ratios (30-60%), and diversification across sectors
- Key metrics to evaluate include dividend yield, payout ratio, dividend growth rate, and company fundamentals, not just the highest yield available
- ⚠️ Common pitfalls include chasing unsustainably high yields, ignoring diversification, and forgetting to account for taxes on dividend income. Morningstar stock or fund analysis
What Is Dividend Investing?
Dividend investing is a strategy that focuses on building a portfolio of stocks that regularly distribute a portion of their earnings to shareholders in the form of cash payments, known as dividends. Think of it as becoming a silent partner in established businesses; companies reward your ownership stake by sharing their profits with you, typically every quarter.
When a company generates profits, management faces a choice: reinvest everything back into the business, or share some of those earnings with the people who own the company (the shareholders). Companies that choose to pay dividends are essentially saying, “We’re profitable enough to both grow our business and reward our investors with cash.”
How Dividends Work: A Simple Example
Let’s say you purchase 100 shares of Company ABC at $50 per share, totaling $5,000 in investment. Company ABC pays an annual dividend of $2 per share, distributed quarterly ($0.50 every three months).
Here’s what happens:
- Every quarter: You receive $50 (100 shares × $0.50)
- Every year: you collect $200 in dividend income
- Your dividend yield: 4% ($200 ÷ $5,000)
You still own all 100 shares, dividends are pure income on top of any price appreciation the stock might experience. This is the beauty of dividend investing: you’re getting paid simply for being a patient owner of quality businesses.
Why Dividend Investing Matters in 2025
The investment landscape has shifted dramatically over the past few years. With inflation concerns, market volatility, and economic uncertainty becoming regular headlines, investors are increasingly seeking strategies that provide both income and stability.
The Power of Passive Income
Passive income through dividend investing offers several compelling advantages:
🔹 Predictable Cash Flow: Unlike hoping for stock price appreciation, dividends provide regular, scheduled payments you can count on.
🔹 Inflation Protection: Quality dividend-paying companies often increase their payouts over time, helping your income keep pace with or exceed inflation.
🔹 Psychological Comfort: During market downturns (and understanding the cycle of market emotions is crucial here), continuing to receive dividend checks provides reassurance and reduces the temptation to sell in panic.
🔹 Forced Savings: Dividend payments create a natural mechanism for accumulating wealth, especially when reinvested.
Historical Performance: The Numbers Don’t Lie
According to Hartford Funds research, dividend-paying stocks have historically outperformed non-dividend-paying stocks. Between 1973 and 2023, dividend growers and initiators returned 10.24% annually, compared to just 3.95% for non-dividend payers.
Even more striking: reinvested dividends have accounted for approximately 40% of the total return of the S&P 500 since 1930. This isn’t a minor detail—it’s a fundamental driver of long-term wealth creation that many investors overlook.
Understanding Key Dividend Metrics
Before building your dividend portfolio, you need to speak the language. These metrics help you evaluate whether a dividend stock deserves your hard-earned money.
Dividend Yield
The dividend yield represents the annual dividend payment as a percentage of the stock’s current price.
Formula: (Annual Dividend Per Share ÷ Current Stock Price) × 100
For example, if a stock trades at $100 and pays $4 annually in dividends, the yield is 4%.
⚠️ Important Note: Higher isn’t always better. An unusually high yield (above 7-8%) often signals danger; the stock price may have crashed due to fundamental problems, or the dividend might be unsustainable.
Payout Ratio
The payout ratio shows what percentage of a company’s earnings goes toward dividend payments.
Formula: (Annual Dividends Per Share ÷ Earnings Per Share) × 100
A healthy payout ratio typically falls between 30-60%. This sweet spot means:
- The company returns meaningful cash to shareholders
- Plenty of earnings remain for growth and reinvestment
- The dividend has a cushion during tough times
Payout ratios above 80% raise red flags—there’s little room for error if earnings decline.
Dividend Growth Rate
The dividend growth rate measures how quickly a company increases its dividend payments over time.
Companies that consistently raise dividends demonstrate:
- Strong, sustainable business models
- Management confidence in future cash flows
- Commitment to rewarding shareholders
A company that has increased its dividend for 25+ consecutive years earns the prestigious title of Dividend Aristocrat, a badge of honor indicating exceptional stability and shareholder focus.
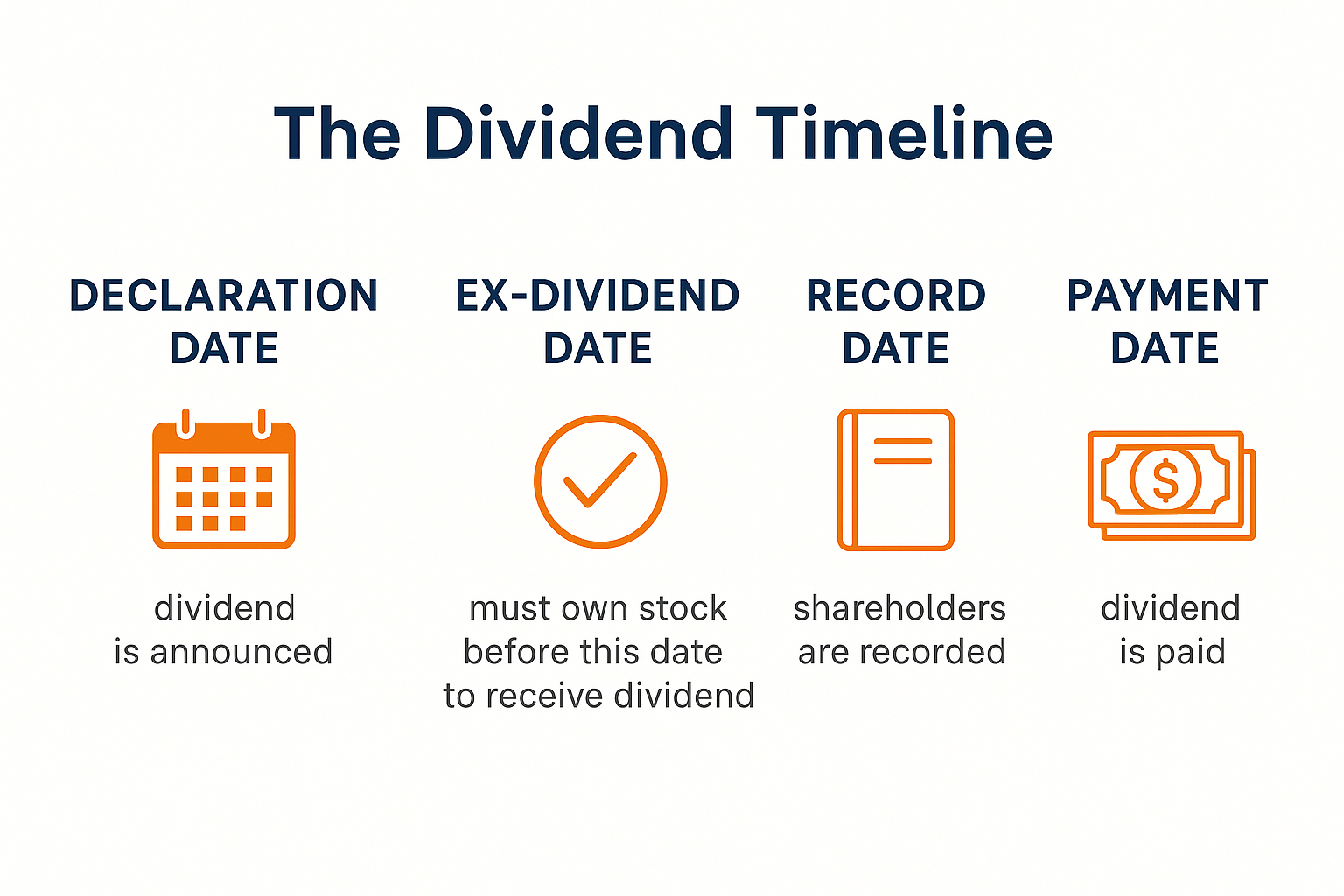
Ex-Dividend Date and Payment Date
Understanding dividend dates prevents confusion:
- Declaration Date: When the company announces the upcoming dividend
- Ex-Dividend Date: The cutoff you must own the stock before this date to receive the dividend
- Record Date: When the company checks its books to see who owns shares
- Payment Date: When the cash hits your account
Pro Tip: If you buy a stock on or after the ex-dividend date, you won’t receive the upcoming dividend payment. The previous owner gets it.
Types of Dividend Stocks
Not all dividend stocks are created equal. Understanding the different categories helps you build a balanced portfolio aligned with your goals.
High-Yield Dividend Stocks
These companies offer above-average yields, typically 5% or higher. They’re attractive to investors prioritizing current income over growth.
Examples: Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), utilities, telecommunications companies
Pros:
- Higher immediate income
- Can be excellent for retirees or income-focused investors
Cons:
- Limited growth potential
- Higher risk of dividend cuts
- Often in mature, slow-growth industries
For more on this category, explore our guide on high-dividend stocks.
Dividend Growth Stocks
These companies may start with modest yields (2-3%) but consistently increase their dividends year after year, often at rates exceeding inflation.
Examples: Johnson & Johnson, Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola
Pros:
- Growing income stream over time
- Often, financially strong companies
- Potential for capital appreciation alongside income
Cons:
- Lower starting yield
- Requires patience to see income growth compound
Dividend Aristocrats
This elite group consists of S&P 500 companies that have increased dividends for at least 25 consecutive years, through recessions, market crashes, and economic upheavals.
Current count: Approximately 67 companies as of 2025
Why they matter: The 25-year requirement filters for exceptional business quality, financial strength, and shareholder-friendly management.
Notable Aristocrats:
- 3M (60+ years of increases)
- Coca-Cola (60+ years)
- Procter & Gamble (65+ years)
- Johnson & Johnson (60+ years)
REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts)
REITs own and operate income-producing real estate. By law, they must distribute at least 90% of taxable income to shareholders, resulting in high yields.
Pros:
- Consistent high yields (often 4-8%)
- Real estate exposure without property management
- Inflation hedge through rent increases
Cons:
- Dividends taxed as ordinary income (less favorable)
- Sensitive to interest rate changes
- Limited growth compared to other sectors
Building Your Dividend Portfolio: Step-by-Step
Ready to start generating passive income? Follow this systematic approach to construct a solid dividend portfolio.
Step 1: Define Your Investment Goals
Before buying a single share, clarify what you want dividend investing to accomplish:
Current Income Focus: Prioritize higher-yielding stocks if you need cash flow now (retirees, supplementing income)
Long-Term Growth Focus: Emphasize dividend growers if you’re accumulating wealth for the future (younger investors, those in their working years)
Balanced Approach: Mix both categories for income today with growth potential tomorrow
Step 2: Determine Your Investment Budget
Start with what you can afford to invest without touching emergency funds or money needed within 3-5 years.
Beginner-Friendly Approach:
- Start with $500-$1,000 if possible
- Commit to regular monthly contributions (even $100/month compounds significantly)
- Many brokers now offer fractional shares, allowing you to invest with minimal capital
Remember: consistency beats timing. Regular investments through all market conditions (dollar-cost averaging) reduce risk and remove emotional decision-making.
Step 3: Research and Select Quality Dividend Stocks
Use these criteria to filter candidates:
✅ Financial Health Checklist:
- Dividend yield: 2-6% (sweet spot for most investors)
- Payout ratio: 30-60% (sustainable range)
- Dividend growth: 5+ years of consecutive increases
- Revenue growth: Positive trend over 5 years
- Debt-to-equity ratio: Below industry average
- Free cash flow: Positive and growing
✅ Quality Indicators:
- Competitive advantages (brand strength, patents, network effects)
- Diversified revenue streams
- Strong market position in their industry
- Competent, shareholder-friendly management
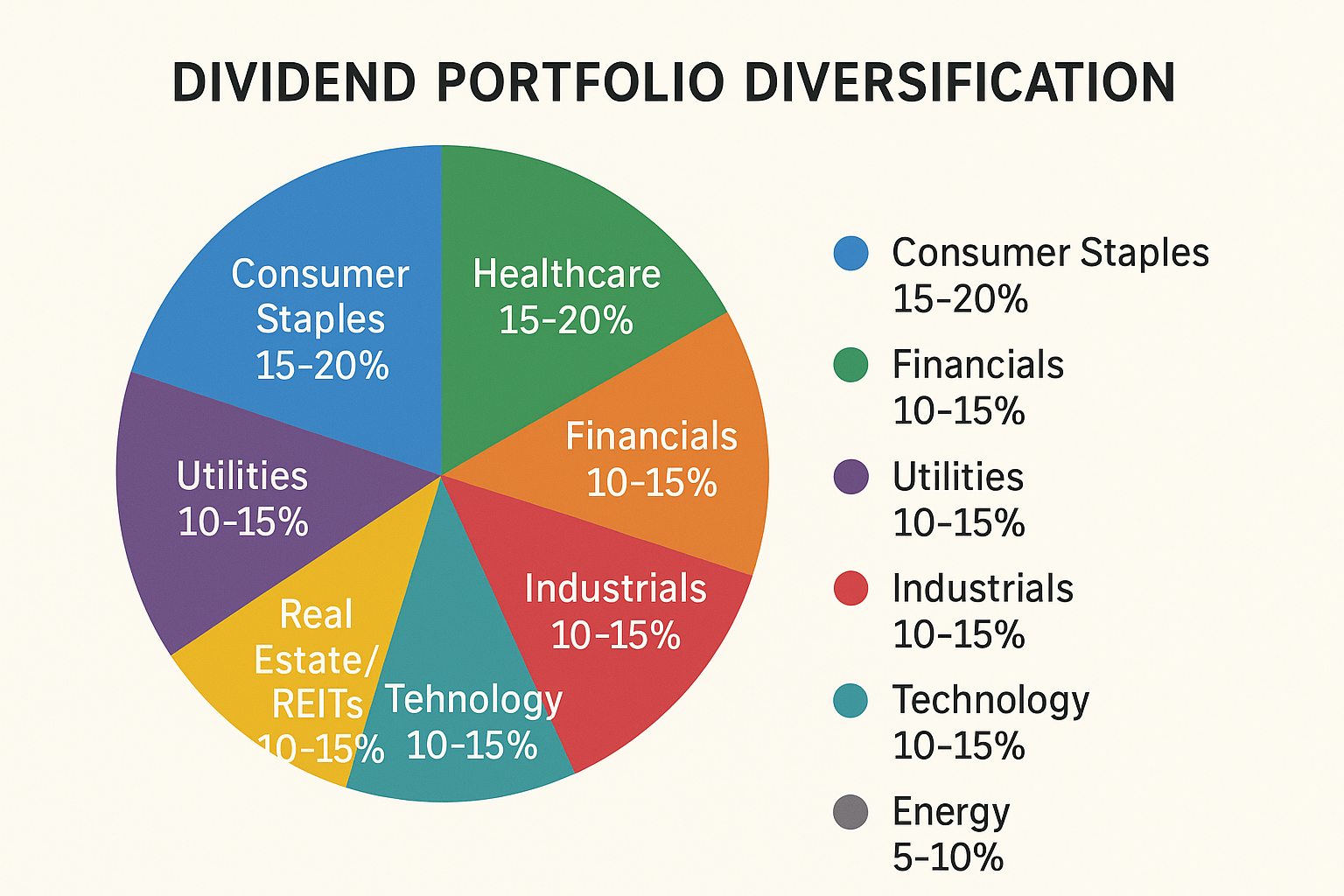
Step 4: Diversify Across Sectors
Never put all your eggs in one basket, or even in one industry basket.
Recommended Sector Allocation:
| Sector | Target Allocation | Dividend Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Staples | 15-20% | Stable, recession-resistant |
| Healthcare | 15-20% | Growing, demographic tailwinds |
| Financials | 10-15% | Cyclical but strong yields |
| Utilities | 10-15% | Stable, high yields |
| Industrials | 10-15% | Economic growth exposure |
| Technology | 10-15% | Growing dividends, lower yields |
| Real Estate (REITs) | 10-15% | High yields, inflation hedge |
| Energy | 5-10% | Volatile but improving |
Diversification protects you when individual sectors face headwinds. When energy struggles, healthcare might thrive. When tech corrects, consumer staples provide stability.
Step 5: Decide on Dividend Reinvestment
When dividends arrive, you face a choice:
Option A: Reinvest (DRIP – Dividend Reinvestment Plan)
- Automatically purchase more shares with dividend payments
- Harnesses compound growth
- Ideal for the wealth accumulation phase
Option B: Take as Cash
- Receive dividends as spendable income
- Provides lifestyle funding or supplements other income
- Ideal for retirement or financial independence
Pro Tip: Many investors reinvest during their working years, then switch to taking cash in retirement. This creates a growing income stream that eventually funds living expenses.
Step 6: Monitor and Rebalance
Dividend investing isn’t “set it and forget it”, though it’s far less demanding than active trading.
Quarterly Review:
- Verify all expected dividends were received
- Check for dividend increase announcements
- Review company earnings reports for red flags
Annual Rebalance:
- Assess sector allocations
- Trim positions that have grown too large
- Add to the underweight sectors or new opportunities
- Replace any companies that cut dividends
The Power of Dividend Compounding
Albert Einstein allegedly called compound interest “the eighth wonder of the world.” When applied to dividends, this power becomes even more remarkable.
A Real-World Example
Consider two investors, both starting with $10,000 invested in a dividend stock yielding 4% annually:
Investor A (Takes dividends as cash):
- Year 1: Receives $400
- Year 10: Still receives $400 annually (assuming no dividend growth)
- Total after 10 years: $10,000 principal + $4,000 dividends = $14,000
Investor B (Reinvests dividends):
- Year 1: Reinvests $400, now owns $10,400 worth
- Year 2: Earns 4% on $10,400 = $416, reinvests
- Year 10: Portfolio value approximately $14,802
- Total after 10 years: $14,802 (all in shares)
The difference? $802, or 20% more wealth, simply from reinvesting.
Now add dividend growth to the equation. If the company increases its dividend by 7% annually (common for dividend growth stocks):
Investor B with dividend growth:
- Year 10: Portfolio value approximately $17,500
- Year 20: Portfolio value approximately $40,000
- Year 30: Portfolio value approximately $90,000
From a single $10,000 investment with no additional contributions, reinvested dividends and dividend growth create nearly $90,000 over 30 years. Add regular monthly contributions, and the numbers become truly life-changing.
Common Dividend Investing Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced investors fall into these traps. Learn from others’ mistakes:
Chasing Yield
The biggest temptation: seeing a 10% yield and assuming it’s a slam dunk.
Reality Check: Abnormally high yields often signal:
- Plummeting stock price due to fundamental problems
- Unsustainable payout about to be cut
- High-risk business model
Better Approach: Focus on sustainable yields (2-6%) with growth potential rather than the highest number available.
Ignoring the Payout Ratio
A company paying out 95% of earnings as dividends has zero margin for error. One bad quarter could force a dividend cut.
Red Flag: Payout ratios above 80%
Safe Zone: 30-60% for most industries (REITs are an exception due to their legal requirements)
Lack of Diversification
Putting all your money in one sector, even if it’s filled with solid dividend payers, exposes you to sector-specific risks.
2008 Example: Investors heavily concentrated in financial stocks saw dividend cuts across the board during the financial crisis.
2020 Example: Energy sector dividends were slashed as oil prices collapsed.
Solution: Spread investments across at least 5-7 different sectors.
Forgetting About Taxes
Dividends create taxable events (unless held in tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s).
Tax Rates (2025):
- Qualified dividends: Taxed at capital gains rates (0%, 15%, or 20% depending on income)
- Ordinary dividends: Taxed at regular income rates (up to 37%)
Strategy: Hold dividend stocks in tax-advantaged accounts when possible, especially high-yield positions and REITs (which pay ordinary dividends).
Panic Selling During Downturns
When markets crash and stock prices fall, dividend investors often panic and sell, locking in losses and forfeiting future dividend payments.
Remember: If the dividend remains intact, temporary price declines don’t affect your income stream. In fact, reinvesting dividends during downturns purchases shares at discount prices.
Understanding why the stock market goes up over time helps maintain perspective during temporary downturns.
Advanced Dividend Strategies

Once you’ve mastered the basics, consider these more sophisticated approaches.
The Dividend Snowball Strategy
Focus exclusively on dividend growth stocks, reinvesting all dividends. Over time, your income “snowballs” as:
- Companies increase dividends
- Reinvested dividends buy more shares
- More shares receive higher dividends
- The cycle accelerates
Timeline Example:
- Year 1: $1,000 annual dividend income
- Year 5: $2,100 annual dividend income
- Year 10: $4,500 annual dividend income
- Year 20: $18,000 annual dividend income
All from an initial investment with no additional contributions—just patience and reinvestment.
The Dividend Capture Strategy
A more active approach where investors buy stocks just before the ex-dividend date to capture the dividend, then sell shortly after.
Caution: This strategy:
- Generates short-term capital gains (taxed at higher rates)
- Incurs trading fees
- Rarely outperforms buy-and-hold for retail investors
- Requires significant time and attention
Verdict: Generally not recommended for beginners or those seeking passive income.
International Dividend Investing
Many foreign companies offer attractive dividends, providing:
- Additional diversification
- Exposure to faster-growing economies
- Often higher yields than U.S. counterparts
Considerations:
- Foreign tax withholding (typically 15-30%)
- Currency risk
- Less regulatory protection
- Higher research difficulty
Easier Approach: International dividend-focused ETFs provide foreign exposure without individual stock research.
Dividend Investing vs Other Strategies
How does dividend investing stack up against alternatives?
Dividend Investing vs. Growth Investing
Growth Investing focuses on companies reinvesting all profits for expansion, with no dividends.
Comparison:
| Factor | Dividend Investing | Growth Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Income | Regular cash flow | None until you sell |
| Volatility | Generally lower | Often higher |
| Tax Efficiency | Less efficient | More efficient (deferred) |
| Psychological Comfort | High (regular payments) | Lower (paper gains only) |
| Best For | Income seekers, retirees | Long-term accumulators |
Verdict: Neither is “better”; both have roles. Many investors hold both dividend and growth stocks for balanced exposure. Federal Reserve macroeconomic or interest rate data
Dividend Stocks vs. Bonds
Both provide income, but with key differences:
Bonds:
- Fixed income (doesn’t grow)
- Lower risk
- No appreciation potential
- Interest taxed as ordinary income
Dividend Stocks:
- Income can grow over time
- Higher risk (stock price volatility)
- Appreciation potential
- Potentially favorable tax treatment
Modern Context (2025): With interest rates having fluctuated significantly, the relative attractiveness shifts. Quality dividend stocks often provide better long-term value than bonds for investors with time horizons exceeding 5-10 years.
For more context on different investment approaches, check out our comparison of index funds vs stocks.
Tax Considerations for Dividend Investors
Taxes significantly impact your actual returns. Understanding the rules helps you keep more of what you earn.
Qualified vs Ordinary Dividends
Qualified Dividends:
- Meet specific IRS requirements (holding period, U.S. or qualified foreign company)
- Taxed at favorable capital gains rates (0%, 15%, or 20%)
- Most common for established U.S. companies
Ordinary Dividends:
- Don’t meet qualified requirements
- Taxed at regular income tax rates (10%-37%)
- Common for REITs, certain foreign companies, and short-term holdings
Tax-Advantaged Account Strategy
Roth IRA:
- Dividends grow tax-free
- Withdrawals in retirement are tax-free
- Best for: Younger investors, dividend growth stocks
Traditional IRA/401(k):
- Dividends grow tax-deferred
- Withdrawals taxed as ordinary income
- Best for: High-yield stocks, REITs
Taxable Brokerage:
- Dividends taxed annually
- Qualified dividends receive favorable rates
- Best for: Dividend aristocrats, qualified dividends
Optimal Strategy: Place high-yield and ordinary dividend payers (REITs) in tax-advantaged accounts; hold qualified dividend payers in taxable accounts if necessary.
Dividend Investing Resources and Tools
Equip yourself with the right resources to research and manage your portfolio effectively.
Screening Tools
Free Resources:
- Dividend.com: Comprehensive dividend data and screening
- Seeking Alpha: Dividend analysis and company research
- Yahoo Finance: Basic dividend information and screening
- FINVIZ: Advanced stock screening with dividend filters
Paid Resources:
- Simply Safe Dividends: Dividend safety scores and analysis
- Morningstar: In-depth company analysis and ratings
Educational Resources
Building knowledge is essential for long-term success. Explore smart money moves and continue expanding your financial education through our comprehensive blog.
Portfolio Tracking
Recommended Apps:
- Personal Capital: Free portfolio tracking with dividend income monitoring
- Sharesight: Detailed dividend tracking and tax reporting
- Spreadsheet: Custom Excel or Google Sheets for complete control
Building Your First Dividend Portfolio: A Practical Example
Let’s put theory into practice with a sample beginner portfolio.
Starting Capital: $5,000
Goal: Balanced income and growth
Time Horizon: 20+ years
Risk Tolerance: Moderate
Sample Allocation:
- Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) – $750 (15%)
- Sector: Healthcare
- Yield: ~3.0%
- Dividend Aristocrat (60+ years)
- Procter & Gamble (PG) – $750 (15%)
- Sector: Consumer Staples
- Yield: ~2.5%
- Dividend Aristocrat (65+ years)
- Realty Income (O) – $500 (10%)
- Sector: Real Estate (REIT)
- Yield: ~5.5%
- Monthly dividend payer
- Microsoft (MSFT) – $750 (15%)
- Sector: Technology
- Yield: ~0.8%
- Strong dividend growth
- JPMorgan Chase (JPM) – $500 (10%)
- Sector: Financials
- Yield: ~2.7%
- Solid dividend growth
- Vanguard Dividend Appreciation ETF (VIG) – $1,000 (20%)
- Diversified dividend growth fund
- Yield: ~2.0%
- Low expense ratio (0.06%)
- Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF (VYM) – $750 (15%)
- Diversified high-yield fund
- Yield: ~3.0%
- Low expense ratio (0.06%)
Portfolio Characteristics:
- Weighted average yield: ~2.8%
- Annual dividend income: ~$140
- Diversification: 7 holdings across multiple sectors
- Mix of individual stocks and ETFs
- Balance of yield and growth potential
Next Steps:
- Set all dividends to reinvest automatically
- Add $200/month in new contributions
- Rebalance annually
- Review holdings quarterly
The Future of Dividend Investing in 2025 and Beyond
The investment landscape continues evolving. Here’s what dividend investors should watch:
Emerging Trends
🔹 Technology Companies Embracing Dividends: Historically, tech companies avoided dividends, preferring to reinvest in growth. That’s changing; Apple, Microsoft, and others now pay meaningful dividends while maintaining innovation.
🔹 ESG and Sustainable Dividend Investing: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors increasingly influence dividend stock selection. Companies with strong ESG profiles often demonstrate better long-term sustainability.
🔹 Rising Interest Rates Impact: When rates rise, dividend stocks face competition from bonds and savings accounts. Quality dividend growers typically weather this better than high-yield stocks.
🔹 Demographic Shifts: As Baby Boomers retire en masse, demand for income-producing investments remains strong, supporting dividend stock valuations.
Sectors to Watch
Healthcare: Aging populations globally create long-term tailwinds for healthcare companies, many of which pay solid dividends.
Technology: Maturing tech giants increasingly return cash to shareholders through dividends, creating a new category of dividend growth opportunities.
Infrastructure: Government spending on infrastructure renewal benefits utilities, industrials, and materials companies—many traditional dividend payers.
Conclusion: Your Dividend Investing Journey Starts Now
Dividend investing offers something increasingly rare in modern finance: a straightforward, time-tested path to building wealth that doesn’t require constant monitoring, complex strategies, or trading expertise. By owning quality companies that share their profits, you create a growing income stream that compounds over time, working for you 24/7, in all market conditions.
The journey from beginner to confident dividend investor doesn’t happen overnight. It requires patience, continuous learning, and the discipline to stick with your strategy through market ups and downs. But the rewards, financial independence, passive income, and the peace of mind that come with owning quality assets make the effort worthwhile.
Your Action Plan
Ready to begin? Here’s your roadmap:
📍 This Week:
- Open a brokerage account if you don’t have one (consider Fidelity, Schwab, or Vanguard for low fees)
- Determine your investment budget and set up automatic monthly transfers
- Research 3-5 dividend stocks using the criteria outlined in this guide
📍 This Month:
- Make your first dividend stock purchase
- Set up dividend reinvestment (DRIP) for automatic compounding
- Create a simple spreadsheet to track your dividend income
- Explore smart ways to make passive income to complement your dividend strategy
📍 This Quarter:
- Add 2-3 more dividend stocks to diversify across sectors
- Review your first dividend payment (celebrate this milestone!)
- Read annual reports from your holdings to deepen company understanding
- Join online dividend investing communities for ongoing education
📍 This Year:
- Build a portfolio of 10-15 dividend stocks or 3-5 dividend ETFs
- Establish a quarterly review routine
- Calculate your total dividend income and projected growth
- Set goals for next year’s portfolio growth
Remember These Core Principles
✅ Quality over quantity: Own fewer excellent companies rather than many mediocre ones
✅ Patience pays: Dividend investing rewards those who think in years and decades, not days and weeks
✅ Reinvest for growth: Compound interest works magic when you give it time
✅ Diversify wisely: Spread risk across sectors and companies
✅ Never stop learning: Markets evolve, companies change, and successful investors adapt
The path to financial freedom through dividend investing isn’t glamorous or exciting. There are no get-rich-quick shortcuts, no secret formulas, no overnight success stories. Instead, there’s something better: a proven, reliable system that has created wealth for millions of ordinary people who simply committed to owning quality businesses and letting time do the heavy lifting.
Your first dividend check might be modest, perhaps $10, $20, or $50. But that check represents something profound: proof that you’re building a system where money works for you, rather than you working exclusively for money. Each subsequent dividend will be a small victory, a step toward the financial future you deserve.
The best time to start dividend investing was ten years ago. The second-best time is today. Take that first step, purchase that first dividend stock, and begin building the passive income stream that will serve you for decades to come.
Your future self, the one receiving regular dividend checks, enjoying financial security, and sleeping soundly knowing quality companies are working for you, will thank you for starting today.
💰 Dividend Portfolio Growth Calculator
Project your dividend income and portfolio growth over time
| Year | Portfolio Value | Annual Dividends | Yield on Cost |
|---|
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute accounting, tax, or investment advice. For decisions that materially affect your business or personal finances, consult a qualified professional.
Author bio
Max Fonji is the founder of TheRichGuyMath.com. 8+ years writing about finance, valuation, and growth strategy. I draw on corporate finance, hands-on business planning, and SEO expertise to build clear, high-quality articles that help business owners and investors. See more: /about.